Are you navigating the complex world of merger and acquisition accounting? Understanding the financial intricacies involved can be a daunting task, but it's essential for a successful transition and integration. Whether you're a seasoned professional or just starting out, grasping the nuances of these transactions will empower you to make informed decisions. So, grab your notepad, and let's dive deeper into this essential topic!

Clarity and precision in financial terms
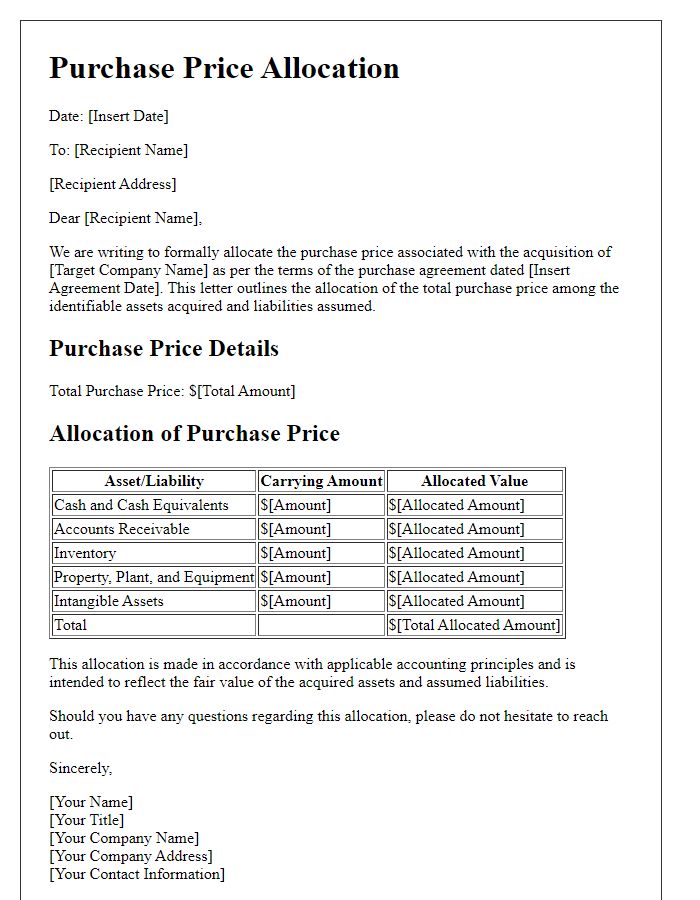
Merger and acquisition accounting involves numerous financial terms that require clarity and precision for accurate valuation and integration of assets and liabilities. The Purchase Price Allocation (PPA) process determines fair values of acquired assets and assumed liabilities, which must be based on current market conditions and specific valuation techniques such as the income approach, market approach, or cost approach. Moreover, the concept of Goodwill (the premium paid over the fair value of identifiable net assets) plays a crucial role, affecting balance sheets significantly after the transaction. The recognition of contingent liabilities also adds complexity, as future obligations tied to the acquisition need proper appraisal to prevent underreporting of risk. Additionally, compliance with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) or Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) is essential to ensure transparency to stakeholders during financial reporting. Accurate reporting can enhance investor trust and provide better insights into the financial health of the merged entities.
Compliance with legal and regulatory standards
In merger and acquisition processes, compliance with legal and regulatory standards is paramount to ensure a smooth transition and operation of merged entities. Entities must adhere to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) regulations, which include timely disclosure of material changes and financial reporting requirements. The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) Guideline ASC 805 mandates the proper accounting for business combinations, emphasizing fair value measurement and asset allocation. Regulatory bodies such as the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) also analyze potential antitrust issues, ensuring that the merger does not create an unfair monopoly. Additionally, local laws and international regulations, such as the European Union's Anti-Trust laws, come into play, necessitating thorough due diligence and regulatory filings to avoid legal repercussions and achieve compliance.
Accurate valuation methods
Accurate valuation methods are crucial in merger and acquisition transactions, significantly impacting financial inputs and strategic decision-making processes. Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) analysis serves as a predictive tool, projecting future cash flows based on financial metrics such as EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization). Comparable Company Analysis (CCA) leverages market data from similar firms within the same industry sector, evaluating valuation multiples like Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratios to derive fair market value. Precedent Transaction Analysis (PTA) examines historical M&A transactions, identifying transaction multiples that illustrate industry trends and buyer behavior. Additionally, assessing intangible assets like brand value and customer relationships is essential; these factors frequently influence overall valuations, particularly in sectors like technology and pharmaceuticals. Thorough due diligence, involving an in-depth review of financial documents and operational performance, further ensures valuation accuracy and mitigates risk in the acquisition process.
Integration and synergy realization
Effective integration following mergers and acquisitions is crucial for realizing synergies and enhancing overall organizational performance. Financial synergy, often projected as a result of cost savings (generally in the 15-30% range) and revenue enhancements, must be systematically assessed during the integration phase. Key performance indicators (KPIs), such as EBITDA margins and return on investment (ROI), serve as benchmarks to evaluate integration success. Establishing a centralized data management system facilitates seamless financial reporting (monthly or quarterly) across merged entities. Cultural alignment between the organizations involved plays a pivotal role, as aligning corporate values can impact employee retention rates significantly, often reflected through turnover statistics. By focusing on operational efficiencies and shared resources, organizations can capitalize on combined purchasing power and optimize supply chain logistics, potentially reducing costs by 10-20%. Regular communication with stakeholders enhances transparency and ensures that strategic goals are consistently met throughout the integration journey.
Communication and stakeholder engagement
Effective communication and stakeholder engagement are vital components during merger and acquisition (M&A) processes. Clarity in messaging ensures all parties understand the rationale behind the merger, potential impacts, and benefits for stakeholders, including employees, investors, suppliers, and customers. Utilizing formal communication channels, such as company-wide emails, webinars, and dedicated Q&A sessions, fosters transparency. Providing stakeholders with timely updates on critical milestones, regulatory changes, and integration plans enhances trust and commitment. Establishing feedback mechanisms, like surveys or focus groups, allows stakeholders to voice concerns, ensuring their perspectives are considered in decision-making. Successful stakeholder engagement not only mitigates resistance but promotes a unified approach toward achieving merger objectives.












Comments