Are you facing concerns about a fiduciary duty breach? It's crucial to understand the responsibilities that come with such roles and the consequences of failing to uphold them. In this article, we'll walk you through the essentials of drafting a clear and effective fiduciary duty breach notice. Stick around to learn how to protect your rights and ensure accountability in your professional relationships!
Breach Description
A fiduciary duty breach occurs when an individual or entity, such as a trustee, business partner, or financial advisor, fails to uphold their legal responsibilities towards another party. This breach may manifest in various ways, such as misappropriation of funds, failure to disclose conflicts of interest, or inadequately managing assets entrusted to them. For instance, in a scenario involving a corporate fiduciary, financial losses exceeding thousands of dollars may arise from poor investment decisions or self-dealing practices. When a financial advisor neglects to act in the best interest of their client, this can lead to significant financial consequences, losing potential gains or incurring avoidable losses. Identifying and documenting such breaches is crucial for pursuing legal remedies or enforcing accountability within the fiduciary relationship.
Parties Involved
In cases involving fiduciary duty breaches, such as in corporate governance or trust management, parties involved typically include the fiduciary party (individual or organization responsible for managing another's assets), the principal (the person or entity to whom the duty is owed), and any beneficiaries (individuals or groups entitled to benefit from the fiduciary's management). A fiduciary could be a corporate officer, a trustee, or an attorney, bound by legal obligations to act in the best interests of the principal. The breach may stem from actions such as self-dealing, lack of disclosure, or failure to act prudently in managing the assets. This scenario often unfolds in contexts like family trusts, business partnerships, or investment management where trust and loyalty are essential.
Legal Obligations
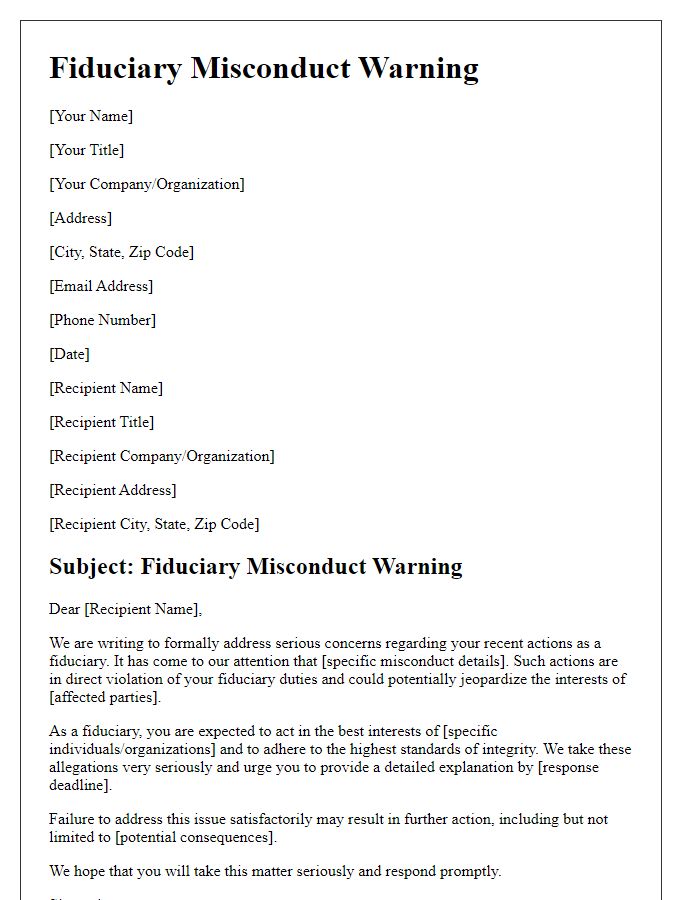
A fiduciary duty breach notice highlights the responsibilities of the fiduciary party, typically outlining specific legal obligations under the law, such as acting in the best interest of the beneficiary. For example, in the context of a corporate board, members are required to avoid conflicts of interest and disclose relevant material facts. When these responsibilities are neglected, such as failing to provide necessary financial reports or making unauthorized decisions, legal repercussions may follow. A breach may stem from actions like self-dealing or misusing confidential information, which can lead to significant financial losses or reputational damage for the beneficiary. Relevant laws, such as the Uniform Trustees' Act, provide a framework for addressing these breaches, including potential remedies like restitution or removal of the fiduciary.
Consequences of Breach
A fiduciary duty breach may result in significant legal consequences for the party involved, potentially leading to a lawsuit for damages. The aggrieved party (the one harmed by the breach) may seek compensatory damages, which are intended to restore any financial losses incurred. In severe cases, punitive damages may also be pursued, intended to punish the breaching party and deter future misconduct. Additionally, the court may impose equitable remedies, such as ordering specific performance or restitution, which require the breaching party to rectify the breach or return any profits obtained through the breach. The breach could also result in loss of trust and reputational damage, impacting both personal and professional relationships, especially in high-stakes environments like financial management or legal representation. Furthermore, regulatory bodies may become involved, leading to potential fines or sanctions if the breach violates specific laws or regulations.
Remedy and Action Steps
When a fiduciary duty breach occurs, prompt notification is critical. This breach involves a trustee or agent acting against the best interests of the beneficiaries, often resulting in financial losses. The notice should detail specific instances of wrongdoing, such as misappropriation of funds or conflicts of interest, which could lead to legal implications. Include actionable steps that the breached party must take, such as returning misappropriated assets within 30 days, providing a comprehensive accounting of funds, or participating in mediation or legal proceedings. Documentation of the breach is essential, including relevant dates, communications, and financial records, all aimed at resolving the issue efficiently while preserving the integrity of fiduciary relationships.
Letter Template For Fiduciary Duty Breach Notice Samples
Letter template of notification regarding fiduciary responsibility violation












Comments