Accrued expenses reconciliation can often seem daunting, but it doesn't have to be! By understanding the key components and processes involved, you can simplify your financial management and ensure your records are accurate. Whether you're a seasoned finance professional or just getting started, mastering this topic is essential for maintaining healthy financial practices. Curious to learn more about effectively reconciling your accrued expenses? Let's dive in!

Header Information
Accrued expenses reconciliation is vital for accurate financial reporting. Components include the company name, registered address, and taxation identification number, ensuring compliance with local regulatory standards. The accounting period (e.g., fiscal year-end March 31, 2023), reflects the specific timeframe of the financial activities being reconciled. Detailed breakdowns involve liabilitarian categories like wages payable and utilities expenses, specifying amounts accrued (e.g., $50,000 for employee salaries) and comparing them with actual disbursements made post-reconciliation. This process ensures that financial statements accurately represent the company's obligations.
Introduction and Purpose Statement
Accrued expenses are liabilities that reflect goods or services received but not yet paid for at the close of an accounting period. Accurate reconciliation of these expenses is crucial for financial reporting and maintaining an accurate balance sheet. This process ensures that all incurred expenses, including payroll, interest, and utilities, are reflected in the financial statements, thereby providing a clear picture of the company's financial obligations. Proper reconciliation aids in identifying discrepancies, supports budget planning, and facilitates compliance with accounting standards, ultimately impacting cash flow management and financial health of the organization.
Detailed Reconciliation Breakdown
Accrued expenses reconciliation provides a comprehensive overview of outstanding financial obligations in accounting. It includes critical line items such as salaries payable, where employees are due $25,000 at the end of the month, and utility bills totaling $5,500 that have not yet been processed. Interest payable may also contribute, estimated at $1,200 for loans from local banks like First National Bank. This detailed breakdown requires meticulous tracking to ensure accuracy in financial statements, aligning with the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). Monthly financial reports should reflect these accrued expenses to provide transparency in fiscal management.
Supporting Documentation List
Accrued expenses reconciliation requires a thorough review of financial documents to ensure accuracy. Key supporting documentation includes invoices (itemized bills detailing services or products rendered), contracts (legal agreements outlining the terms of services), purchase orders (authorizations confirming the purchase of goods), and internal memos (communications detailing expenses incurred). Additionally, payroll records (documents outlining employee wages and benefits) and bank statements (financial records from accounts showing transactions) provide crucial insights for validating accrued expenses. Reports generated from accounting software, such as QuickBooks or SAP, offer detailed breakdowns of accrued expenses, aiding in effective reconciliation. Accurate organization of these documents enhances transparency during the audit process.
Closing and Contact Information
Accrued expenses reconciliation ensures accurate tracking of unpaid financial obligations, essential for financial statements. Commonly, this process involves examining accounts payable and accrued liabilities. In financial accounting, accrued expenses represent costs incurred but not yet paid, affecting companies like ABC Corporation in their quarterly reports. Closing entries summarize these reconciliations, often performed on specific dates, such as the end of fiscal year on December 31. Contact information for the finance department, typically includes direct phone lines, emails of key personnel, and operational hours, ensuring clear communication for any discrepancies or inquiries. Proper documentation is critical, including invoices and receipts, to validate entries during audits.
Letter Template For Accrued Expenses Reconciliation Samples
Letter template of accrued expenses reconciliation for financial reporting.

Letter template of accrued expenses reconciliation for internal auditing.

Letter template of accrued expenses reconciliation for year-end closing.

Letter template of accrued expenses reconciliation for cash flow analysis.
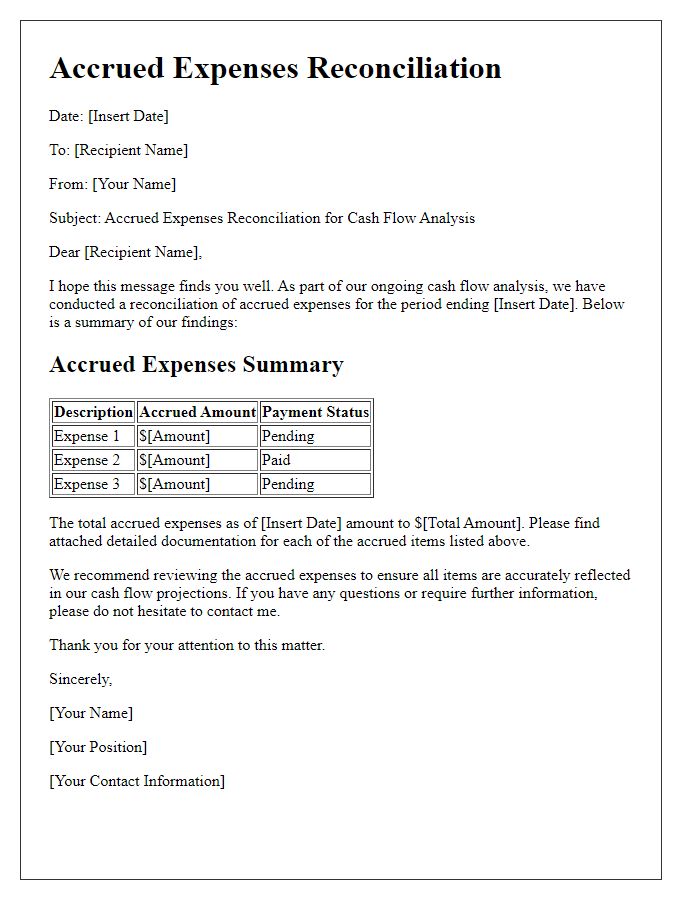
Letter template of accrued expenses reconciliation for management review.

Letter template of accrued expenses reconciliation for stakeholder communication.

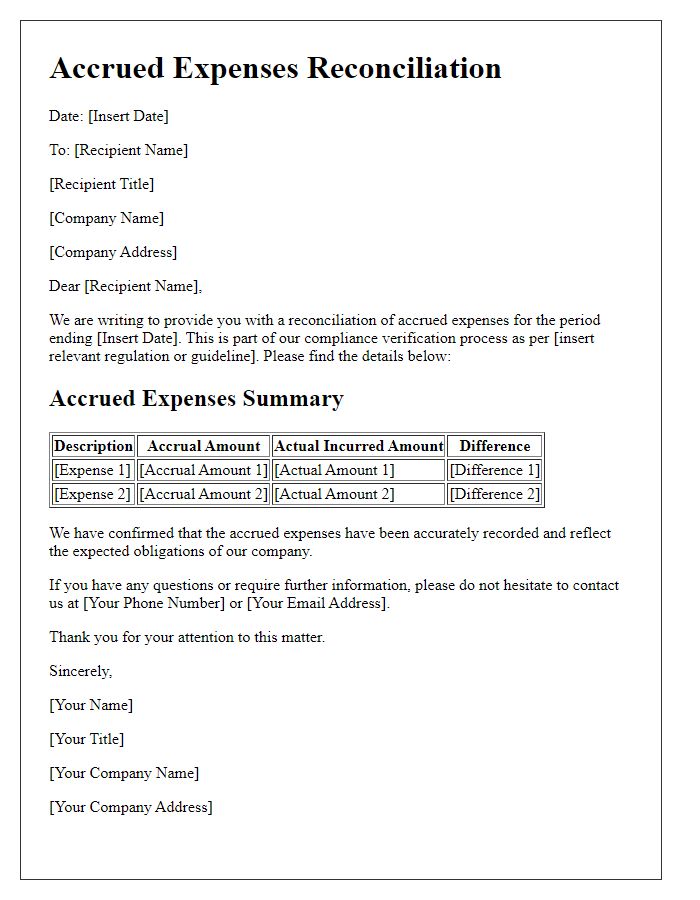
Letter template of accrued expenses reconciliation for compliance verification.


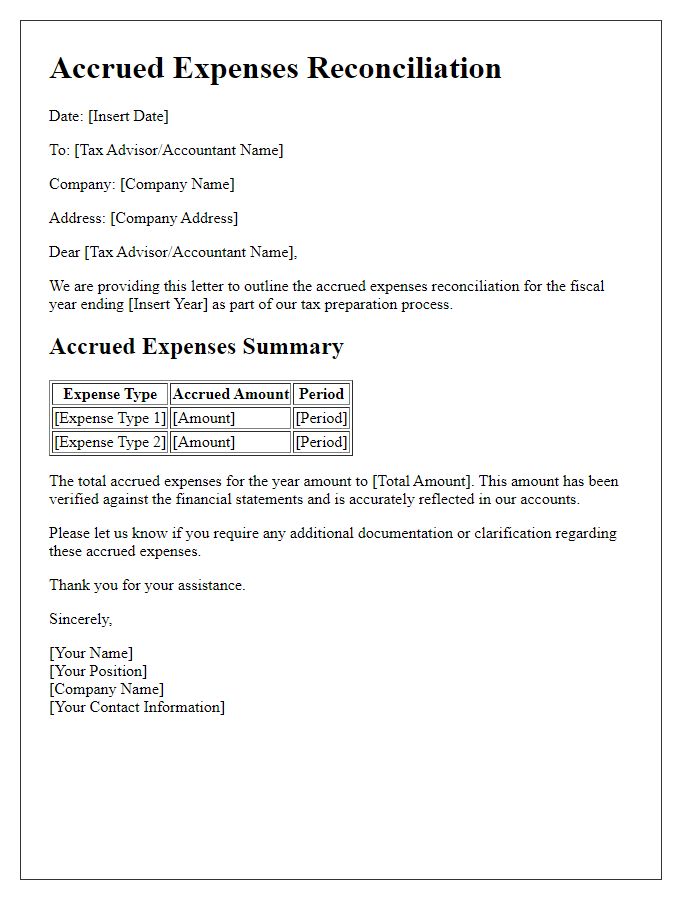



Comments