Hey there! As we dive into the quirky world of cryptocurrency, it's essential to stay on top of your tax reporting obligations. Cryptocurrencies can be thrilling, but they also come with some important financial responsibilities that you won't want to overlook. Whether you've bought, sold, or simply held your digital assets, knowing how to report them correctly is crucial to keeping the taxman happy. So, grab your favorite drink and let's explore what you need to know about cryptocurrency tax reporting!

Personal and Contact Information
Cryptocurrency tax reporting requires precise documentation of transactions, profits, and losses for compliance. Accurate records of personal identities, such as full names, addresses, and Social Security numbers, are essential to meet IRS requirements in the United States. Contact information must include active phone numbers and email addresses to facilitate communication with tax authorities. Reporting gains, losses, and holdings typically centers around exchanges like Coinbase or Binance, where transaction history provides necessary data. Tax year milestones, including April 15 deadlines for individual filings, highlight the importance of timely submissions to avoid penalties. Use of accounting software can streamline the preparation of IRS Form 8949, detailing each cryptocurrency transaction.
Summary of Cryptocurrency Transactions
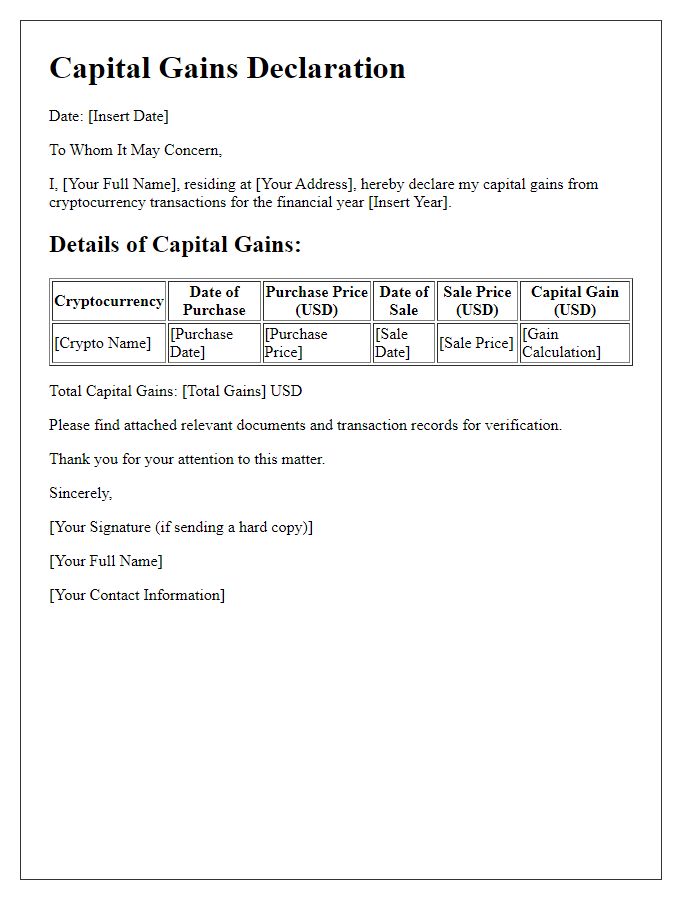
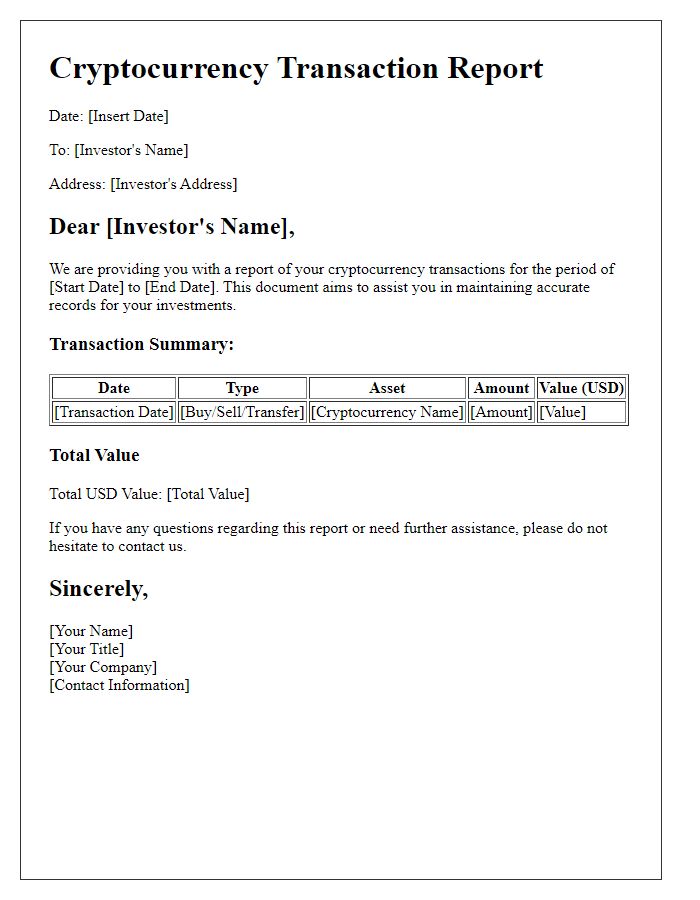
Cryptocurrency transactions require detailed reporting for tax compliance in jurisdictions such as the United States, where the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) mandates accurate documentation. The summary should include a total of transactions conducted, highlighting significant activities throughout the year, such as purchases, sales, and exchanges. Each entry must specify the date, type of cryptocurrency (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum), transaction amount, and USD market value at the time of each transaction. Additionally, expenses related to mining activities, trading fees, and losses or gains should be clearly outlined to facilitate proper capital gains tax calculations. Collectively, these figures will contribute to a comprehensive tax return and ensure compliance with federal regulations.
Tax Liability and Calculation Methodology
Cryptocurrency tax reporting is crucial for compliance with regulations set forth by governing tax authorities, such as the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in the United States. Tax liability arises from capital gains incurred during trading, selling, or converting crypto assets like Bitcoin, Ethereum, or Litecoin. The calculation methodology includes determining the fair market value (FMV) of cryptocurrencies at the time of transaction, which may fluctuate significantly due to market volatility--Bitcoin's price reached over $60,000 in 2021. Taxpayers must report all transactions accurately on forms such as Form 8949 and Schedule D to avoid penalties. Recordkeeping of dates, amounts, and involved parties is essential in establishing a clear audit trail for potential reviews by tax authorities.
Legal Regulations and Compliance Instructions
Cryptocurrency tax reporting has become essential due to evolving legal regulations set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and various international tax authorities. Taxpayers must report cryptocurrency transactions, including sales, exchanges, and mining activities, accurately. Transactions exceeding $600 may require Forms 1099-K or 1099-MISC to be filed. Furthermore, understanding the classification of cryptocurrencies under IRS guidelines, as either property or currency, is crucial for compliance. Failing to report accurately can lead to audits and potential penalties, emphasizing the importance of keeping detailed records of transactions, wallet addresses, and relevant dates to adhere to legal requirements. Taxpayers should consult IRS Publication 561 for comprehensive guidance on the fair market value assessments and reporting obligations.
Deadline for Response and Payment
Cryptocurrency tax reporting requirements have gained urgency as regulators tighten compliance measures worldwide. In the United States, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) mandates that taxpayers declare their cryptocurrency transactions, including sales and exchanges, on Form 1040. The deadline for response and payment is typically April 15, with penalties for late submission reaching up to 5% of unpaid tax per month, not exceeding 25%. Essential to this process is the accurate reporting of gains and losses, derived from the fair market value at the time of transactions. Cryptocurrency exchanges, such as Coinbase and Binance, offer transaction histories which facilitate tax calculations, while the total capital gains must be reported separately from ordinary income. Taxpayers are advised to seek professional guidance to navigate potential complexities related to their specific trading activities and to avoid costly mistakes.
Letter Template For Cryptocurrency Tax Reporting Notice Samples
Letter template of cryptocurrency tax reporting requirements for individuals











Comments