Are you considering a tuition payment plan to ease the financial burden of education? Many students and families are exploring flexible options that allow for manageable monthly payments instead of a hefty lump sum. This approach not only alleviates stress but also helps budget more effectively throughout the academic year. If you're curious about how to set up a tuition payment plan and what it entails, read on for detailed guidance and tips!

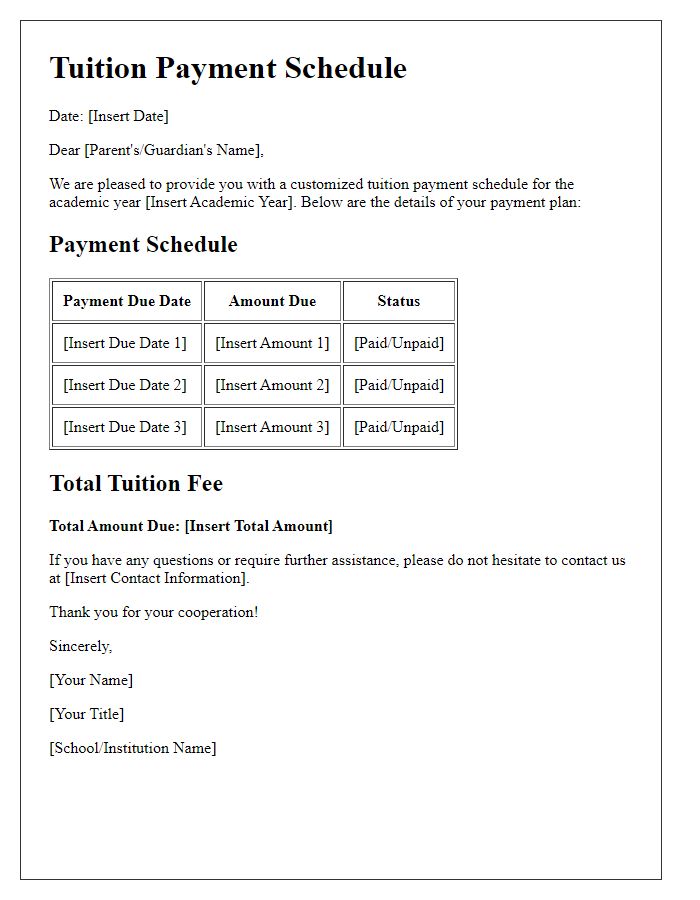
Payment Schedule
Developing a structured payment plan for education expenses ensures financial clarity and aids students in managing tuition fees. The payment schedule typically outlines the total cost of tuition, which may exceed amounts like $10,000 per semester for private colleges. A breakdown of payment dates, often coinciding with the academic calendar, includes due dates such as August 1st for the fall semester and January 1st for spring classes. Payment options may involve monthly installments, with a potential deposit requirement, usually around 10% of the total tuition, to secure enrollment. Additionally, details regarding late fees, interest rates, or consequences for missed payments promote responsibility and accountability in handling financial commitments. Furthermore, information about potential scholarships or financial aid programs can provide additional support to address tuition-related burdens.
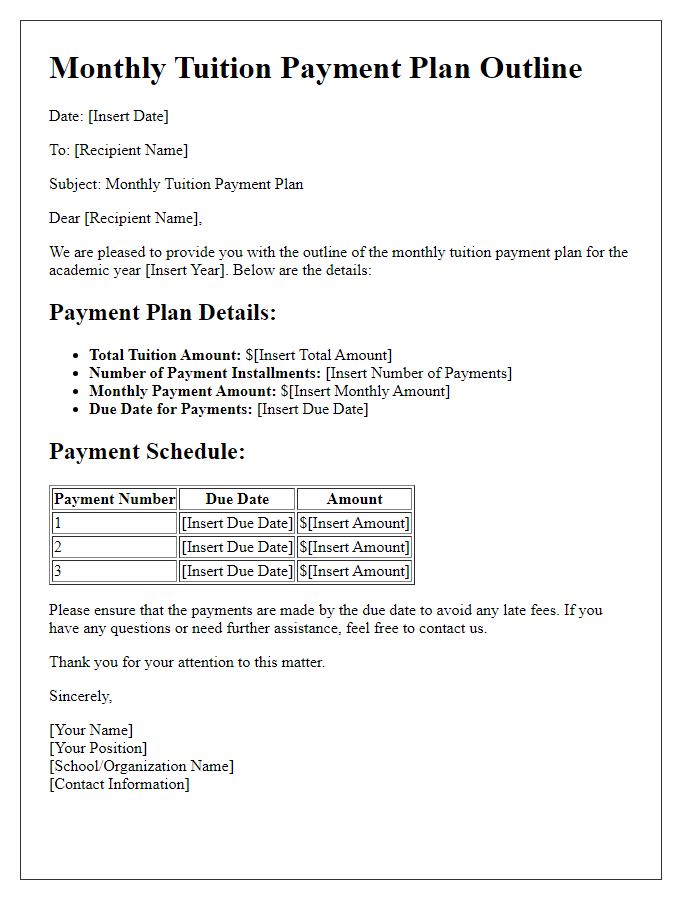
Payment Methods
Tuition payment plans offer a flexible solution for managing educational expenses, particularly for institutions like universities or private schools. Various payment methods include credit cards, bank transfers, or automated payment systems, allowing families to choose what best suits their financial situation. Monthly installments break down the total tuition fee, enabling easier budgeting over the academic year. For instance, a typical payment plan might span ten months, dividing a $20,000 tuition fee into manageable payments of $2,000. Institutions often provide online portals for seamless transactions, ensuring security and transparency. Additionally, some organizations may offer discounts for early payments or additional fees for late payments, emphasizing the importance of understanding the specific terms and conditions associated with each payment method.
Late Payment Penalties
Late payment penalties can significantly impact a tuition payment plan, affecting financial obligations for institutions and students alike. A common penalty is a late fee of 5% applied to unpaid balances after the due date, commonly set at the start of each semester (e.g., August 15 for fall and January 15 for spring). If payment remains overdue beyond 30 days, additional penalties may accrue, potentially reaching up to 10% of the total outstanding amount. Institutions often reserve the right to suspend access to academic records or future registrations if payments are persistently late. In some cases, specific payment deadlines must be met to qualify for financial aid or scholarships, further complicating the implications of late payments. Regular communication and clear policies can help ensure accountability and understanding of the consequences associated with delayed tuition payments.
Contact Information
Creating a tuition payment plan can ease the financial burden for families managing educational expenses. Accurate records of contact information (such as phone numbers and email addresses) are crucial for effective communication between educational institutions and families. Detailed payment schedules (monthly or quarterly) may include amounts due, payment methods (credit card, bank transfer), and deadlines. Educational institutions often create a formal agreement outlining terms and conditions, ensuring clarity on penalties for late payments and options for financial aid or scholarships that may assist in the process.
Agreement Terms
A tuition payment plan is a structured agreement detailing the financial terms regarding educational expenses, typically established between an educational institution and a student or guardian. This agreement outlines payment schedules, specifying amounts due per term, semester, or month, along with due dates. It includes policies on late fees (commonly ranging from $25 to $100 depending on the institution), payment methods accepted (credit card, bank transfer, etc.), and any potential penalties for missed payments. Additionally, it may highlight implications of non-compliance, such as withdrawal from courses or holds on academic records. Essential to the plan is clarity on total tuition costs, including potential additional fees (lab fees, registration fees) associated with the program, ensuring all parties have a thorough understanding of their financial obligations in relation to the educational services being provided.











Comments