Are you ready to simplify your remote work experience? Setting up a remote desktop can seem daunting, but it doesn't have to be! With the right instructions at hand, you can access your files and applications from anywhere in just a few easy steps. So grab your device, and let's dive into the setup process togetherâread on for our detailed guide!

Clear step-by-step process
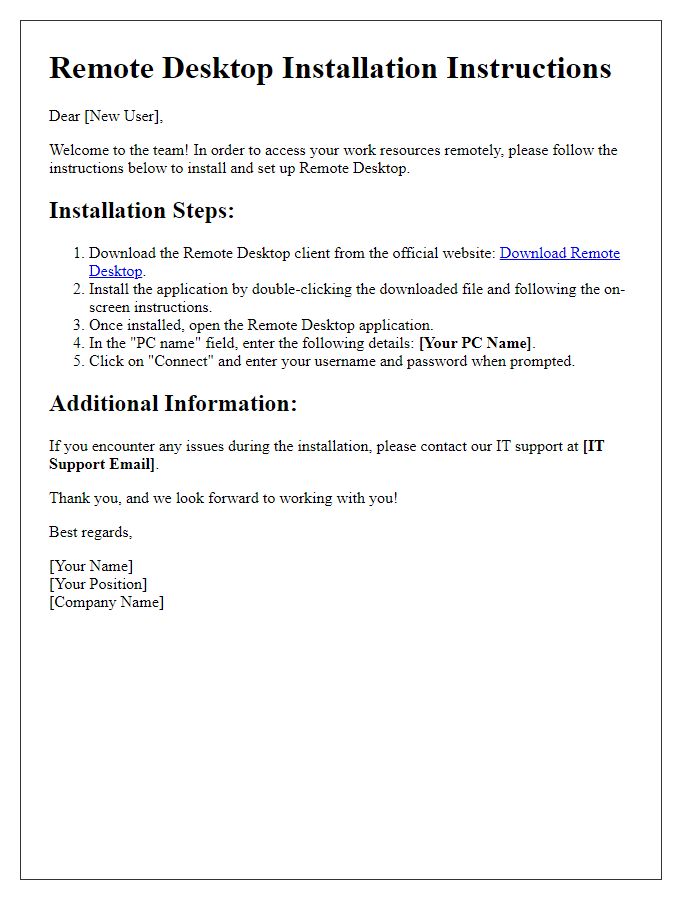
Remote desktop setup instructions provide users with a clear, structured guide to connect to a remote computer via Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). First, ensure that the target computer, typically running Windows 10 Pro, has Remote Desktop enabled in System Properties. Navigate to Settings, select System, and click on Remote Desktop; toggle the option to allow remote access. Next, note down the computer's IP address, accessible through Command Prompt with the command "ipconfig" (look for the IPv4 Address). On the client computer, open the Remote Desktop Connection application, enter the IP address of the target computer, and click 'Connect'. When prompted, input the appropriate user credentials (username and password) for the remote computer. Lastly, confirm the connection and enjoy remote access, ensuring a stable internet connection (minimum 1 Mbps recommended).
Required software and tools
To establish a remote desktop connection, essential software includes Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) applications and virtual private network (VPN) tools. RDP applications, like Microsoft Remote Desktop, enable users to access a computer from another device seamlessly, with versions available for Windows, macOS, and mobile platforms. Setting up a VPN, such as Cisco AnyConnect or OpenVPN, ensures a secure environment for remote access, protecting data integrity and privacy over public networks. Additionally, installed software must be compatible with operating systems, including Windows 10 or macOS Monterey versions. The process often includes configuring firewalls and ensuring the target machine allows remote connections, enhancing security and functionality.
Security measures and credentials
Remote desktop setups require strict security measures, especially in environments handling sensitive data, such as corporate networks. It is essential to use strong credentials; usernames (ideally 8-20 characters, mixing letters and numbers) should not be easily guessable, while passwords must follow complexity requirements (at least 12 characters, including uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters). Configuring network settings such as VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) adds an extra layer of security by encrypting data during transmission. Enable two-factor authentication (2FA), requiring users to verify their identity through an additional method, usually a mobile device. Regular updates of both the operating system and remote desktop software (like Microsoft Remote Desktop or TeamViewer) are crucial to patch vulnerabilities. Firewalls should be correctly configured to allow only necessary ports (commonly TCP 3389 for RDP) and IP addresses. Periodic security audits of the remote desktop session logs (including user access times and activities) help in identifying unauthorized attempts.
Troubleshooting tips
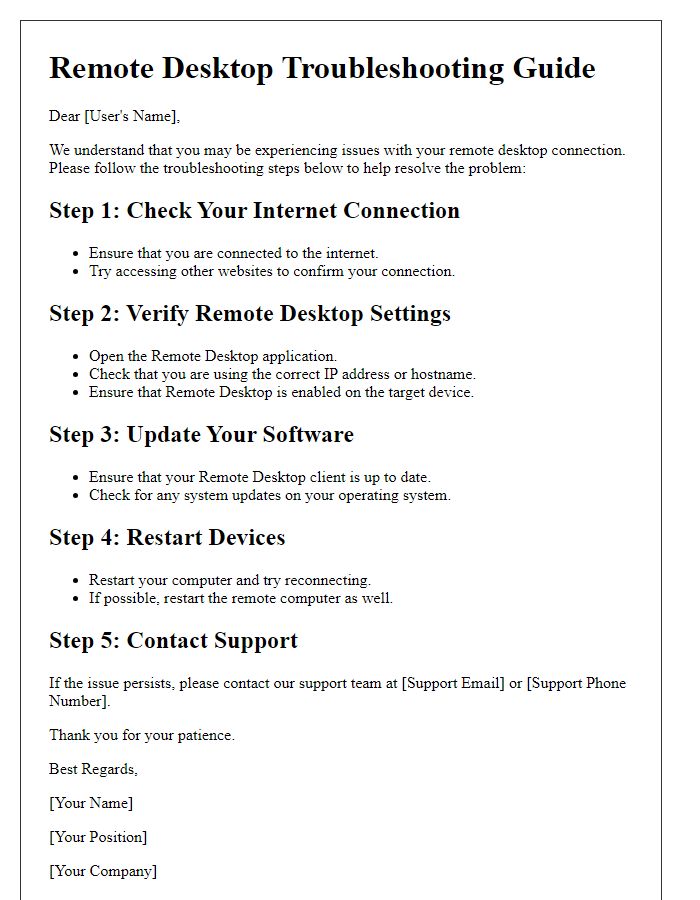
Remote desktop setup can encounter various issues that impede connectivity and functionality. Common problems include failure to connect, which may arise from incorrect IP addresses (ensure the IP address is accurate, like 192.168.1.1) or firewall settings (check Windows Firewall or third-party antivirus rules). User permissions need verification, confirming that the remote user has adequate privileges (Windows 10 Pro requires appropriate user group membership). Network configurations should be validated, especially router settings (port forwarding might be necessary for Remote Desktop Protocol, default port 3389). Additionally, ensure that Remote Desktop is enabled on the host machine by navigating to System Properties under "Remote Settings." Performance issues such as lag can occur due to insufficient bandwidth on the internet connection, often needing a speedtest (aim for at least 5 Mbps for optimal performance). For security purposes, consider using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to safeguard remote access. Remember to update software regularly to patch security vulnerabilities and improve compatibility.
Contact information for support
Remote desktop setup requires attention to detail for effective connections and performance. Ensure the remote desktop software, such as Microsoft Remote Desktop, is installed on both devices. Proper configuration settings should be applied, including enabling Remote Desktop on the host machine (Windows 10 or higher) and adjusting firewall settings for port 3389. For any complications during setup or connection issues, support is available at techsupport@example.com, or by calling the dedicated helpline at (555) 123-4567 during office hours, which are Monday through Friday, 9 AM to 5 PM EST. Always have your machine's IP address and operating system version on hand when contacting support for faster resolution.
Letter Template For Remote Desktop Setup Instructions Samples
Letter template of remote desktop installation instructions for new users.
Letter template of remote desktop connection settings for work-from-home.











Comments