Are you looking for a seamless way to confirm your inventory orders? Sending an effective order confirmation letter not only enhances communication but also solidifies your professional relationship with suppliers. This template will guide you in crafting a concise and clear message that leaves no room for misunderstanding. Ready to get started? Let's dive into the details!

Inventory details and quantities
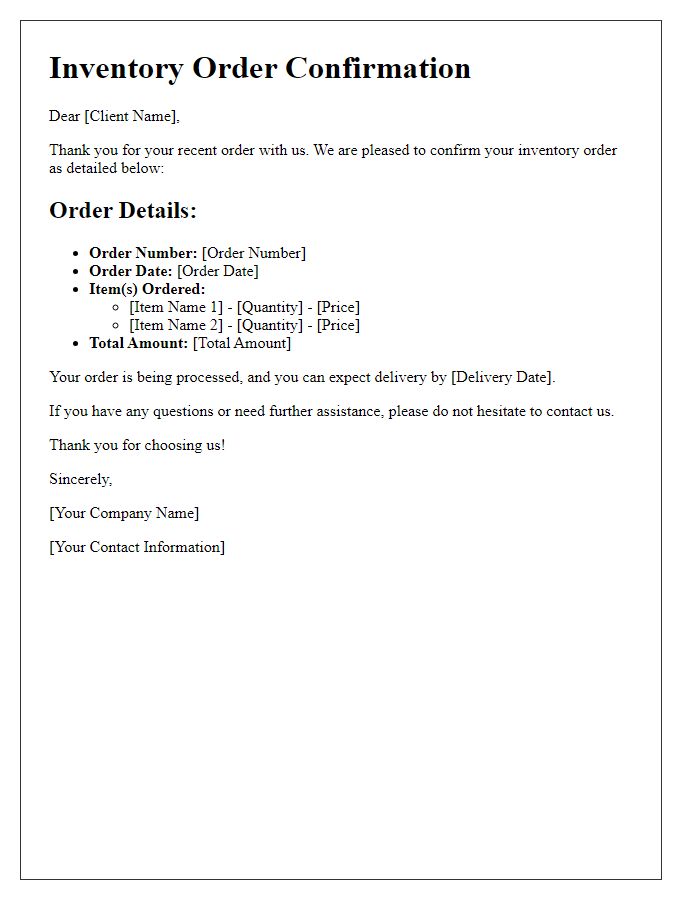
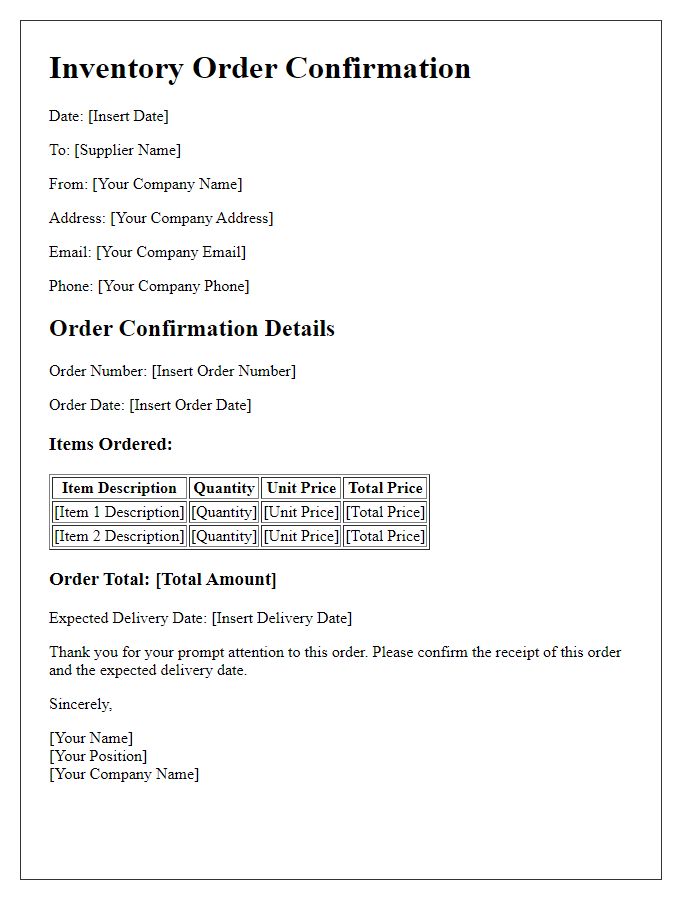
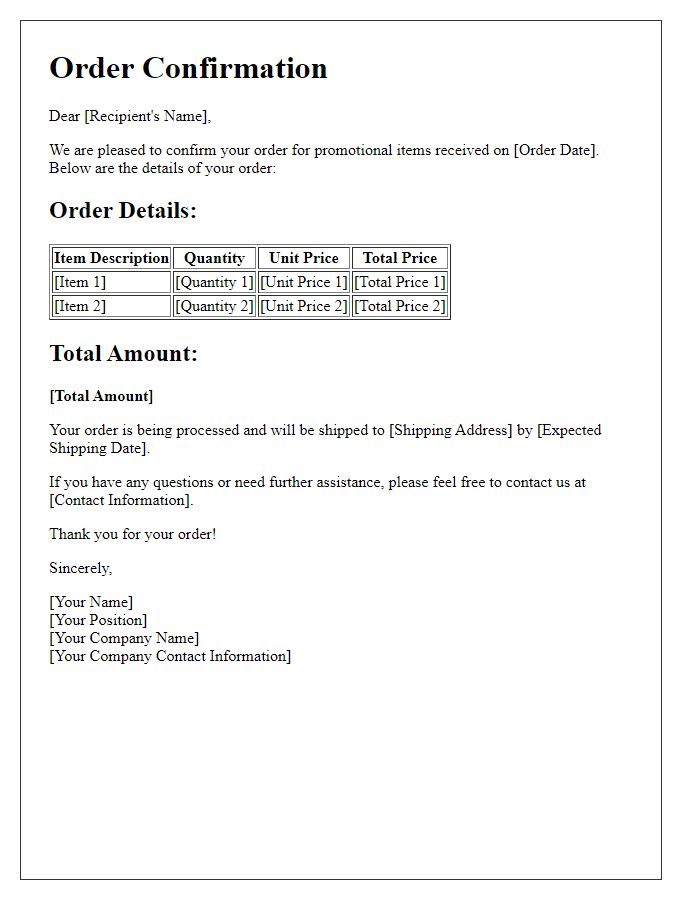
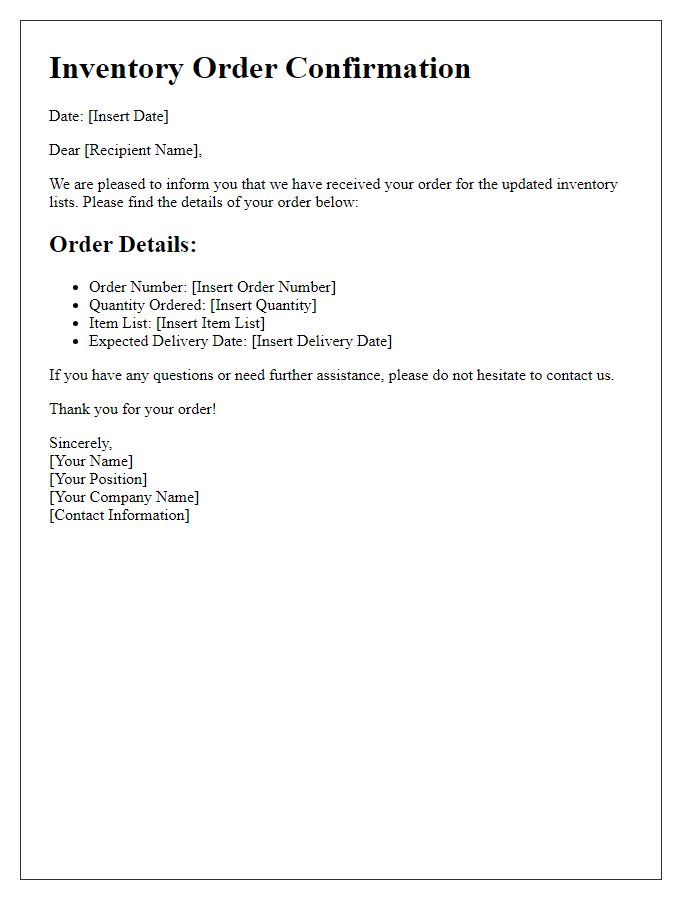
Inventory order confirmations play a crucial role in retail and supply chain management, ensuring accurate tracking of products and quantities. Essential components include product names like "Widget A" or "Gadget B", alongside specific quantities such as "150 units" or "300 pieces". Details should specify order numbers for better reference, for instance, "Order No. 00123", while encompassing delivery dates like "November 15, 2023". Including warehouse locations, such as "Warehouse 1, Seattle", enhances clarity. Confirmation of payment terms like "Net 30 days" and shipping methods, for example, "UPS Ground", are vital for transaction integrity.
Supplier and company contact information
Efficient inventory order confirmation involves clear communication between suppliers and companies. The contact information often includes essential details such as the supplier's name, address, email, and phone number, which facilitate smooth transactions. The company's contact information must also be precise, featuring the business's name, location, contact person, direct line, and official email. This clarity ensures all parties can address any inquiries or discrepancies promptly. Proper documentation helps maintain a streamlined supply chain process, ensuring timely delivery of goods and accurate record-keeping essential for inventory management.
Order reference number
Order reference number serves as an essential identifier for tracking inventory requests. It typically consists of a unique alphanumeric code designed to streamline order management processes across various systems. Accurate entry of this number ensures seamless communication between suppliers and customers, reducing the likelihood of errors in processing. For instance, an order reference number could help connect procurement teams with specific inventory requests, facilitating timely delivery of products such as electronic components or office supplies. This play an important role in maintaining organizational efficiency and customer satisfaction in industries from retail to manufacturing.
Confirmation of payment terms and conditions
In the realm of inventory management, confirmation of payment terms and conditions is critical to ensure a smooth transaction process. Payment terms generally encompass details such as net payment periods, commonly 30 or 60 days, and acceptable payment methods, which may include bank transfers, credit cards, or checks. Conditions may also refer to discounts offered for early payments, typically 2% off within 10 days for businesses placing bulk orders, or late payment penalties, which can incur fees after a specified grace period. Furthermore, clarity regarding delivery schedules and any relevant shipping costs can prevent misunderstandings. Establishing these terms not only fosters trust between suppliers and clients but ensures compliance with financial protocols and inventory management best practices.
Estimated delivery date and shipping method
Incorporating detailed inventory order confirmations, businesses can enhance communication clarity, particularly concerning estimated delivery dates and shipping methods. For example, a company might indicate the estimated delivery date as November 15, 2023, allowing for adequate planning around stock replenishment in retail locations. The shipping method might specify services like UPS Ground, which typically offers delivery within 1 to 5 business days depending on regional proximity. Including order tracking number, such as 1Z999AA10123456784, aids in monitoring delivery status for timely adjustments in inventory management systems. Accurate details ensure seamless operational flow in supply chain processes.









Comments