As the year draws to a close, it's that time again when we gather our financial documents and prepare for tax season. Staying organized now will save you time and stress later, ensuring that you're ready to navigate the ins and outs of your tax obligations. Whether you're an individual taxpayer or a business owner, understanding the specifics of your end-of-year tax information is crucial. So, let's dive in and explore everything you need to know to tackle this year's tax preparation with confidence!

Taxpayer Identification Information
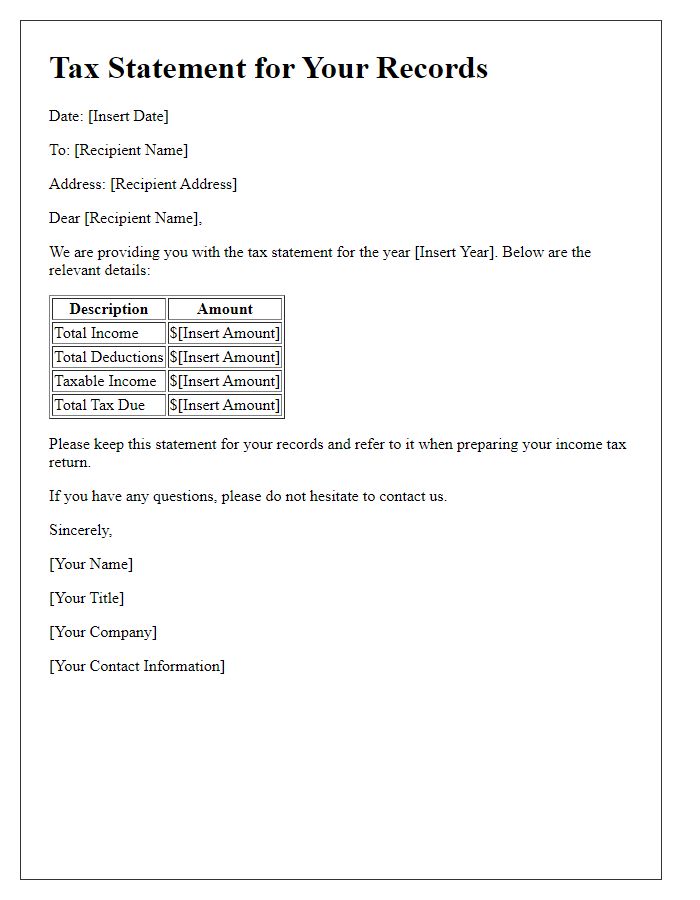
Year-end tax information is crucial for accurate filing during tax season. Taxpayer Identification Numbers (TIN) such as Social Security Numbers (SSN) or Employer Identification Numbers (EIN) serve as unique identifiers for individuals and businesses, respectively. Proper documentation is essential to avoid discrepancies with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), based in Washington D.C. The IRS requires all taxpayers to provide accurate TINs on forms such as 1040, indicating taxable income for the year. Failure to report a correct TIN can result in delay of refunds or penalties amounting to hundreds of dollars. Ensuring that your TIN is updated and verified can save potential complications when filing between January and April, commonly known as tax season.
Summary of Income and Expenses
End-of-year tax information includes a detailed Summary of Income and Expenses that provides a comprehensive overview of financial performance for the tax year, typically from January 1 to December 31, in various sectors such as business or personal finance. This summary outlines total income generated, including wages, dividends from investments, and any rental income from properties, in addition to expenses like operational costs, utilities, and travel expenditures necessary for business activities. Accurate records and documents such as bank statements, receipts, and invoices become crucial in compiling this summary, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements set by entities like the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in the United States. Timely submission of this summary aids in expediting the tax filing process, potentially resulting in faster refunds or minimized liabilities.
Deductions and Credits Overview
End-of-year tax information, particularly concerning deductions and credits, is pivotal for individuals and businesses preparing for tax season. A comprehensive overview of deductions, such as mortgage interest (potentially amounting to thousands of dollars) and student loan interest (with a maximum deduction of $2,500), provides significant financial relief. Credits like the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC), impacting millions of low- to moderate-income workers with potential credits of up to $6,728, significantly reduce tax liability. Accurate tracking of expenses throughout the year, as well as understanding eligibility requirements for specific credits, ensures taxpayers maximize their financial benefits. Notable changes in tax law (such as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017) continue to influence deductions and credits available in 2023, necessitating informed decision-making during tax preparation.
Tax Payment and Refund Details
At the end of the fiscal year, individuals can review their financial obligations and potential refunds related to their tax filings. Tax payment deadlines, typically falling on April 15 for the previous calendar year in the United States, require timely submissions for accurate calculations of owed amounts. Refunds can vary widely based on numerous factors including adjusted gross income, deductions, and credits claimed, with the IRS reporting average refunds around $3,000 in recent years. Taxpayers often utilize tax filing software or consult professional accountants to ensure compliance with federal regulations, with forms such as the 1040 serving as the primary income tax return. Additionally, state tax obligations must be accounted for, as many states have their own filing deadlines and tax regulations, which can impact overall refunds or additional payments due. Familiarity with these details can empower taxpayers to better prepare and maximize their financial outcomes for the following year.
Important Tax Filing Deadlines
Important tax filing deadlines act as vital reminders for taxpayers to ensure compliance with federal regulations, such as those set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in the United States. The deadline for individual tax returns, Form 1040, typically falls on April 15, unless it falls on a weekend or holiday, which can shift the due date to the next business day. Additionally, tax filers who require an extension must submit Form 4868, extending the deadline to October 15. Business entities, such as partnerships, must file Form 1065 by March 15. Taxpayers should keep in mind estimated tax payments due on April 15, June 15, September 15, and January 15 of the following year to avoid penalties. Timely submission of these forms and payments ensures taxpayer compliance with federal and state tax laws, avoiding costly fines and interest.











Comments