Hey there! We all know that staying compliant is crucial in today's fast-paced business environment, especially when it comes to working with suppliers. An effective compliance audit can streamline processes, ensure high standards, and foster stronger partnerships. In this article, we'll break down the essentials of scheduling a supplier compliance audit that meets all the necessary criteria. So, stick around to discover valuable tips and insights that can elevate your auditing game!

Audit Objective and Scope
The Supplier Compliance Audit Schedule outlines the systematic evaluation of supplier adherence to industry standards and regulations, specifically targeting quality control practices, environmental management systems, and labor conditions. The audit objective encompasses assessing compliance with legal requirements, ensuring alignment with contractual obligations, and evaluating alignment with international standards such as ISO 9001 (quality management) and ISO 14001 (environmental management). The scope includes on-site assessments at supplier facilities located in key regions such as Southeast Asia and Eastern Europe, focusing on production processes, supply chain transparency, and workforce rights. Key documentation to be reviewed will include quality assurance records, environmental impact assessments, and employee handbooks, providing a comprehensive overview of the supplier's ability to meet organizational and regulatory benchmarks.
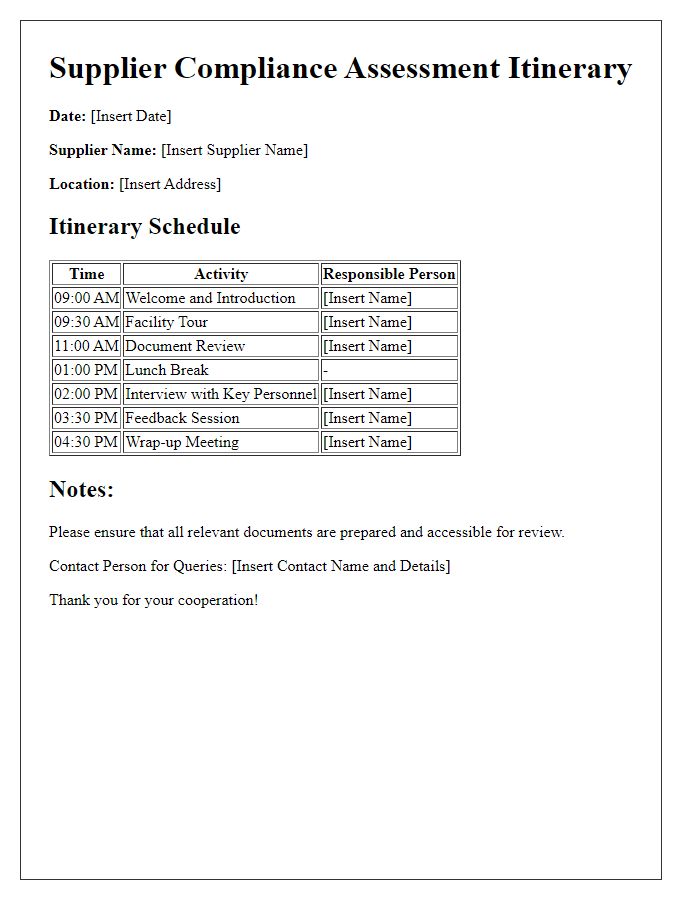
Audit Schedule and Duration
Supplier compliance audits are crucial for ensuring adherence to industry standards and regulations. The audit schedule typically spans several days, with specific dates designated for different suppliers, such as XYZ Manufacturing on March 15, 2024, and ABC Supplies on March 20, 2024. Each audit lasts approximately eight hours, encompassing document review, facility inspections, and staff interviews. Key aspects evaluated include safety protocols, quality control processes, and compliance with environmental regulations, such as ISO 14001 standards. The audit team, consisting of two lead auditors and one quality assurance specialist, will assess supplier practices, ensuring they align with company policies and regulatory requirements. Follow-up meetings are scheduled one week after each audit to discuss findings and establish improvement plans.
Required Documentation and Records
Supplier compliance audits necessitate the submission of comprehensive documentation and records to ensure adherence to regulatory standards. These documents include Quality Management System (QMS) manuals, which outline the protocols and procedures for maintaining product quality, as well as Certificates of Compliance, verifying alignment with industry regulations such as ISO 9001. Additionally, suppliers must provide records of training programs, including participant lists and training dates, essential for workforce competency verification. Product specifications and test results must be available for review, showcasing compliance with safety and performance standards. Furthermore, inventory management records, showing stock levels and turnover rates, offer insight into operational efficiency and supply chain integrity. It is crucial to maintain precise financial documents, such as invoices and payment records, which can assist in evaluating financial stability and ethical practices within the supply chain.
Team Members and Roles
The Supplier Compliance Audit Schedule involves a structured team comprising various roles essential for the audit process. The Audit Lead coordinates overall activities, ensuring adherence to compliance standards, while the Compliance Officer oversees the evaluation of supplier practices against regulatory frameworks. The Quality Assurance Specialist assesses product quality metrics, identifying deviations from set specifications, and the Data Analyst compiles audit data for insightful reporting. The Logistics Coordinator manages the scheduling of site visits to supplier facilities, facilitating timely and efficient audits. Each member plays a critical role in ensuring suppliers meet contractual and regulatory obligations, fostering a culture of accountability and excellence.
Compliance Standards and Criteria
The compliance audit schedule for suppliers focuses on evaluating adherence to specific standards, including ISO 9001 (Quality Management Systems) and ISO 14001 (Environmental Management Systems). This systematic review occurs at predetermined intervals, typically annually, ensuring that suppliers meet quality, safety, and environmental regulations. Audits comprise document reviews, on-site inspections, and interviews with personnel. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as defect rates and incident reports are assessed to gauge compliance levels. Auditors from certification bodies, such as SGS or Bureau Veritas, conduct these evaluations, which inform the decision-making process regarding supplier relationships and contract renewals. Results influence corrective actions, mitigating risks associated with non-compliance, and enhancing overall supply chain integrity.












Comments