When it comes to exporting goods, understanding the intricacies of shipping documentation is essential for ensuring a smooth process. These crucial documents not only facilitate international trade but also ensure compliance with customs regulations. Whether you're a seasoned exporter or just starting, having the right documentation can save you time and money. Curious to learn more about the specific templates and details you'll need for successful export shipping?

Exporter's Company Information
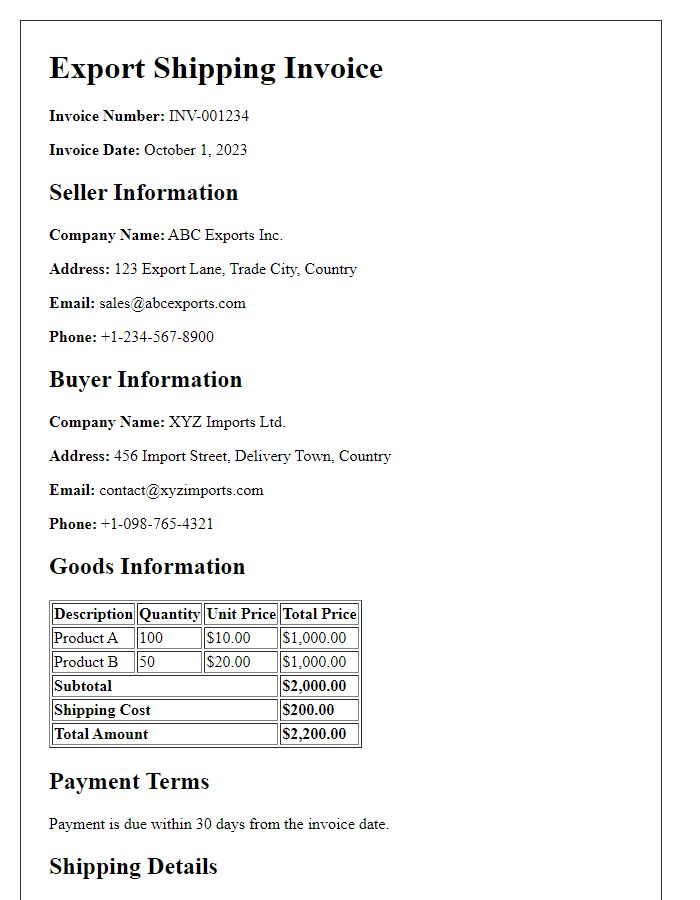
Exporter's company information plays a crucial role in international trade, ensuring compliance with regulations. This includes the legal business name, registered address, and contact details of the exporter, which must adhere to the standards of both the origin and destination countries. The company's registration number, often required for customs clearance, verifies its legitimacy. It's essential to include the tax identification number (TIN) or VAT number, as this facilitates related tax processes. Moreover, details about the exporter's industry classification, such as NAICS or SIC codes, provide insight into the nature of the goods being shipped, ensuring proper categorization. Always update this information to reflect any changes in the company's status to avoid shipping complications.
Consignee Details
Consignee details are essential for export shipping documentation, ensuring the accurate identification of the recipient. This information typically includes the consignee's full name, business address, and contact number. When exporting goods internationally, specific details such as the country of destination (for example, Canada), postal code, and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) value may be required for customs clearance. Furthermore, businesses must provide their tax identification number for compliance purposes, alongside any specific instructions related to the handling of goods upon arrival. These details facilitate smooth logistics, minimize disruptions, and maintain regulatory compliance during transit.
Description of Goods
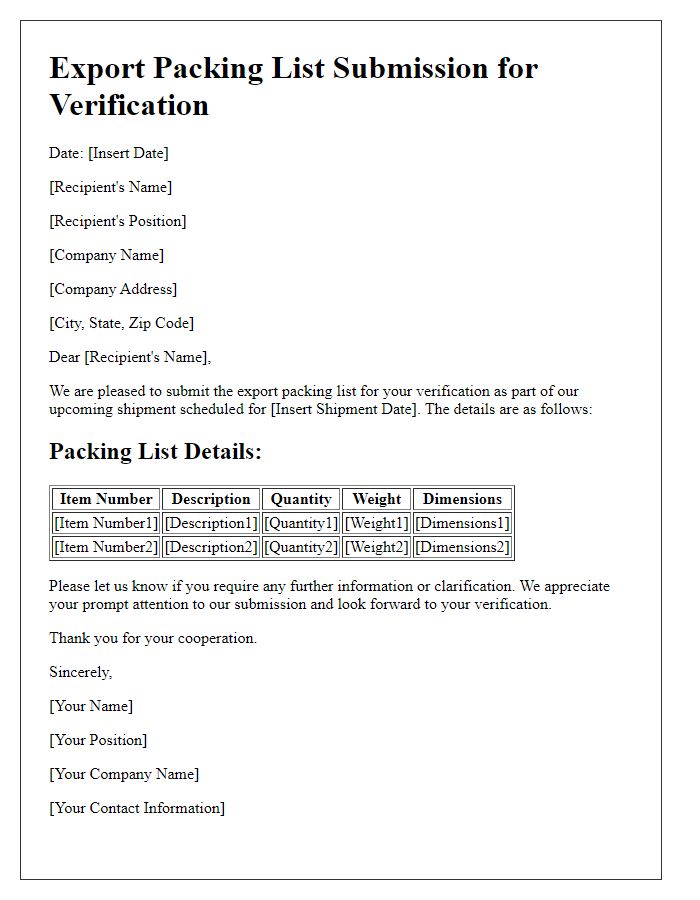
Export shipping documentation requires an accurate description of goods to ensure compliance with international trade regulations. Essential aspects include the product names, such as "electronic components" or "textile fabrics," along with quantities, which must specify units like "50 cartons" or "200 kilograms." Additional details encompass the relevant Harmonized System (HS) codes assigned by the World Customs Organization for categorization. Precise origins must be indicated, such as "manufactured in Vietnam" or "sourced from Germany." Furthermore, including product specifications, like dimensions or material compositions, enhances clarity. Each item should also have proper identification, such as serial numbers or batch numbers, facilitating traceability through the supply chain, and ensuring adherence to safety standards or quality certifications, especially for regulated items like pharmaceuticals or machinery.
Shipment Details (incoterms, mode of transport)
The export shipping documentation requires precise shipment details, including Incoterms, which define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Common terms like FOB (Free On Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) dictate the points of risk transfer. For mode of transport, methods such as sea freight, air freight, or trucking should be specified, each affecting cost and delivery time. Including details such as container numbers or flight numbers enhances traceability. Accurate shipment dimensions and weight provide necessary information for logistics planning, ensuring compliance with international shipping regulations and smooth customs clearance processes at destination ports.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance Information
Export shipping documentation necessitates stringent adherence to legal and regulatory compliance standards. Countries like the United States (specifically the Bureau of Industry and Security) and the European Union maintain specific guidelines that govern the export of goods. Compliance with the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) mandates proper classification of products, such as dual-use items, electronics, or defense-related materials. Additionally, the Export Control List (ECL) identifies goods requiring a license for international shipment. Accurate completion of customs declarations, including Harmonized System (HS) codes and country of origin, is critical for avoiding penalties. Exporters must also be aware of sanctions imposed by agencies like the Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) which prohibits trade with designated entities. Engaging with freight forwarders familiar with local regulations can facilitate compliance, mitigating legal risks during international transport operations.
Letter Template For Export Shipping Documentation Samples
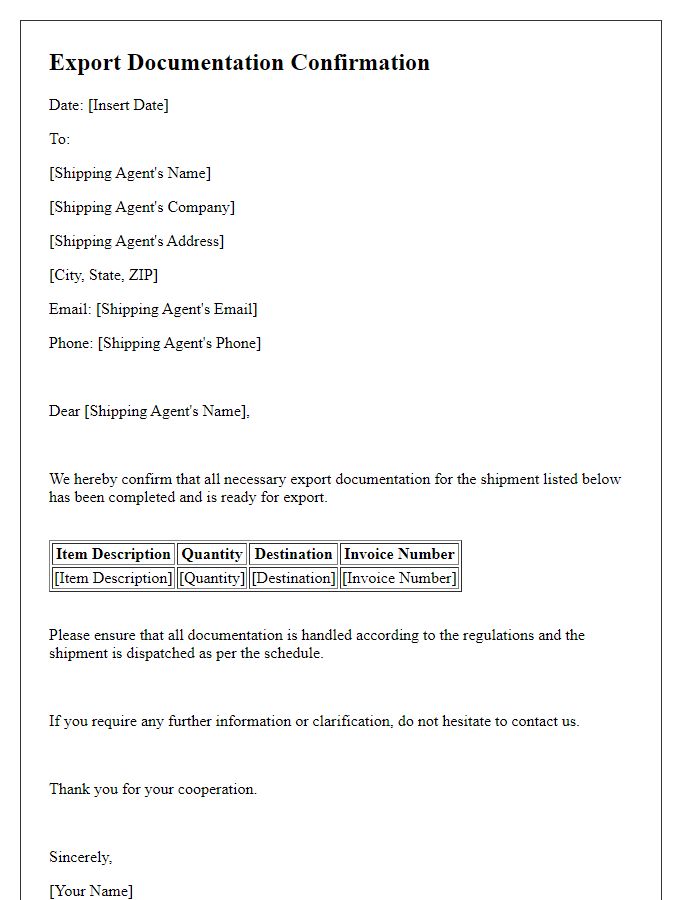
Letter template of export documentation confirmation for shipping agents.
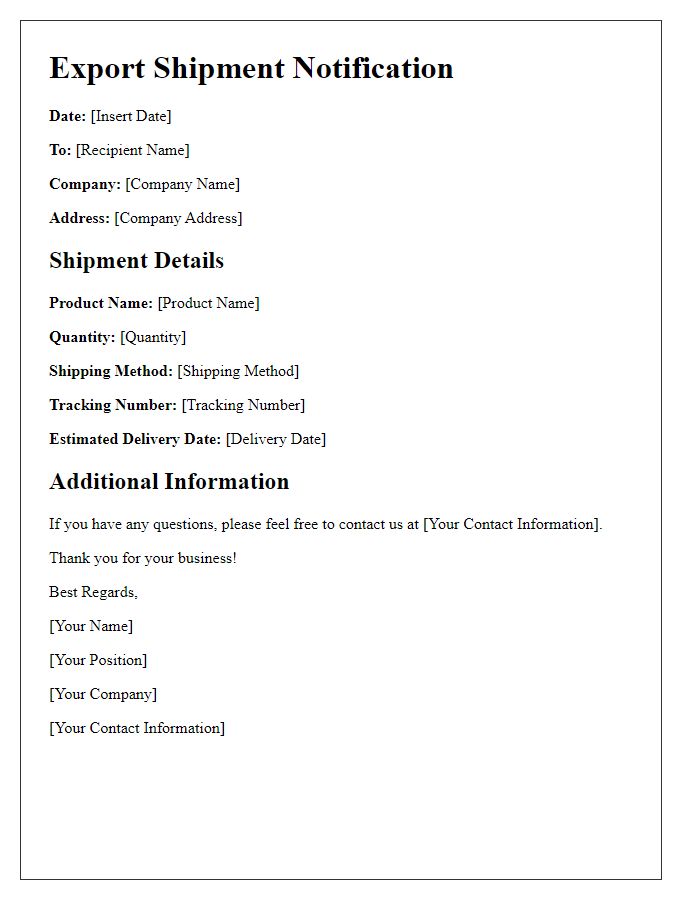
Letter template of export shipping authorization for third-party handlers.









Comments