Are you in the process of drafting a loan repayment contract but aren't sure where to start? Creating a clear and concise letter can help both the lender and borrower understand the terms of repayment, ensuring a smooth financial arrangement. In this article, we'll guide you through a helpful template that covers all the essential elements, making it easy to navigate your loan obligations. So, let's dive in and explore how you can structure your loan repayment contract effectively!

Loan repayment terms and conditions
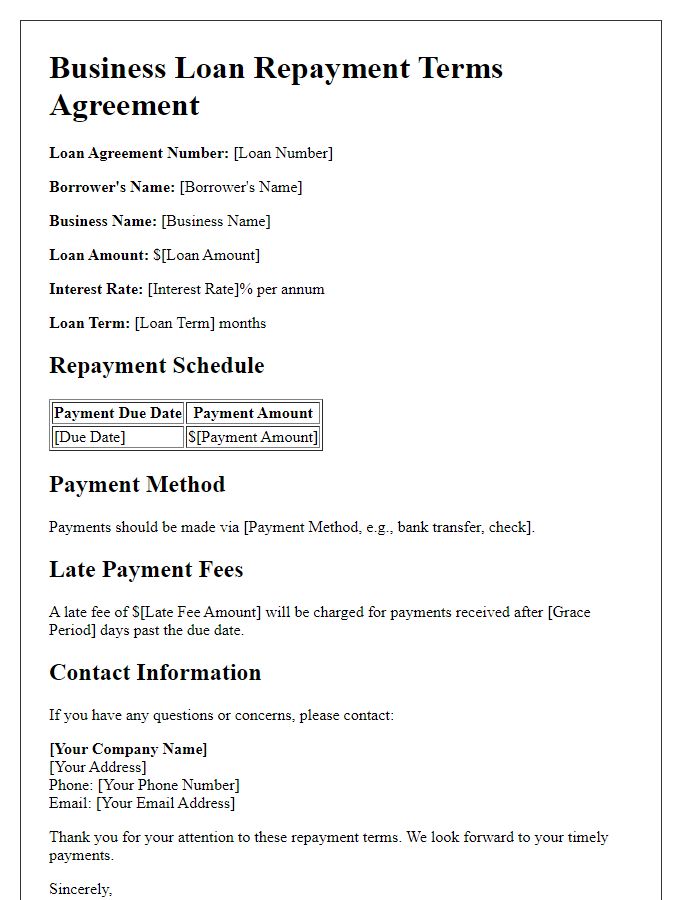
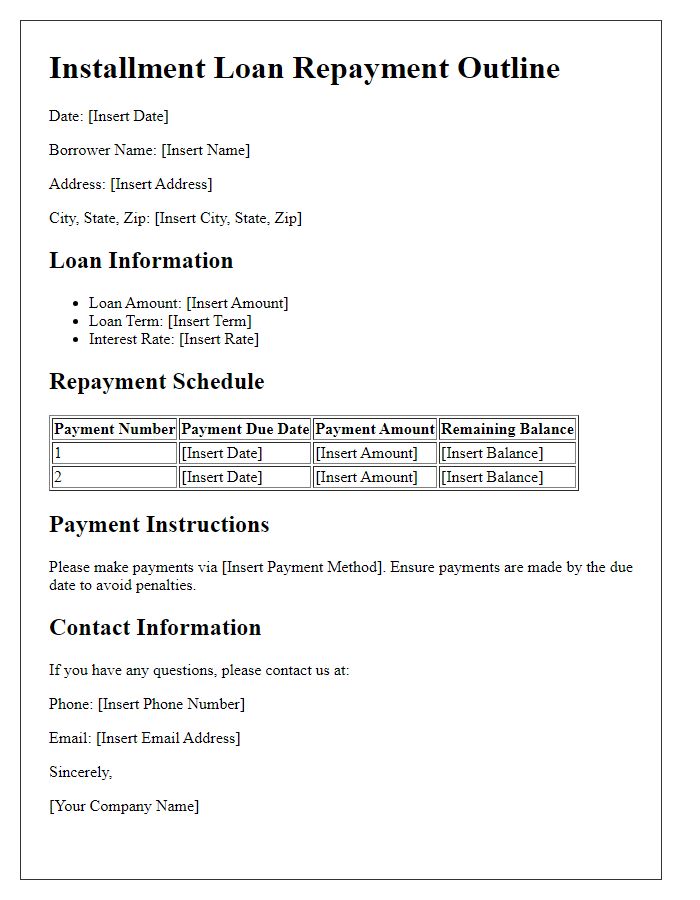
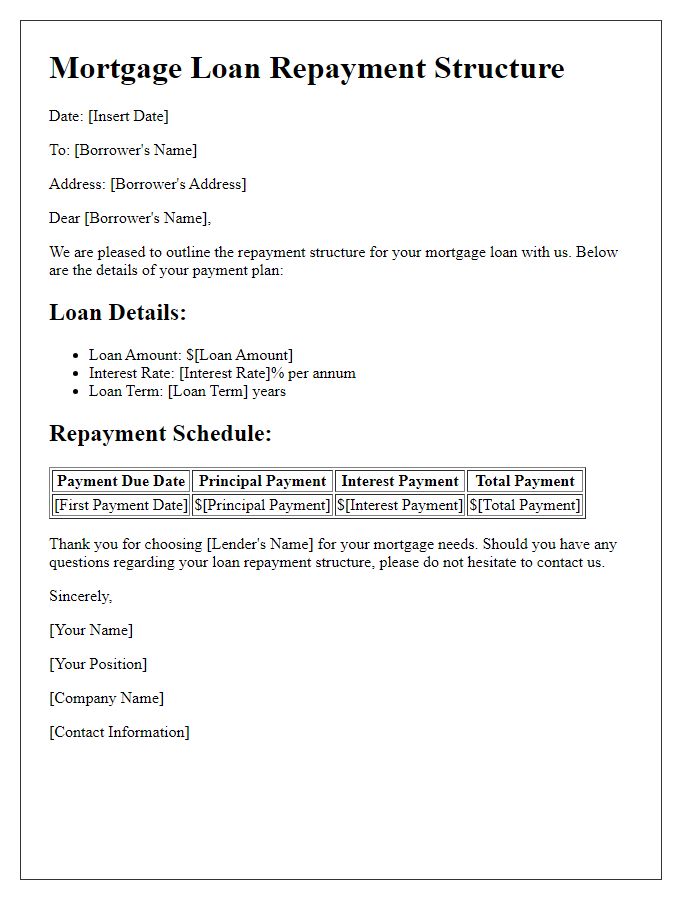
Loan repayment agreements outline essential terms, defining borrower and lender responsibilities, payment schedules, and interest rates. Typically, the document specifies the principal amount, originating date, and specific interest rate applicable, such as 5% annually. It indicates the total payment period, often ranging from 12 to 60 months, with monthly payment due dates. Consequences of late payments are essential, potentially including late fees or increased interest. Additionally, clauses regarding early repayment options permit borrowers to pay off the loan ahead of schedule without penalty, enhancing financial flexibility. Proper documentation ensures legal protection for both parties, particularly in disputes or financial difficulties, underscoring the importance of explicit terms in financial agreements.
Borrower and lender information
In a loan repayment contract, detailed information regarding both the borrower and lender is essential for ensuring clarity and legal validity. The borrower, typically an individual or organization, must be identified with full legal name, address, contact number, and Social Security Number (SSN) or Tax Identification Number (TIN). The lender, often a financial institution or private individual, should similarly provide their full legal name, address, contact number, and relevant business registration number if applicable. The contract must specify the amount loaned, interest rates (often expressed as an annual percentage rate), and repayment terms, which may include the repayment schedule, due dates, and penalties for late payments. It is also crucial to detail any collateral involved, outlining the specific items or properties securing the loan. A mutual agreement regarding dispute resolution procedures should also be included to manage potential conflicts effectively.
Interest rate and repayment schedule
A loan repayment contract typically outlines essential details such as the interest rate and repayment schedule. The interest rate, often expressed as an annual percentage rate (APR), indicates the cost of borrowing, with rates varying based on creditworthiness, loan type, and market conditions; for instance, rates can range from 3% to 20% depending on these factors. The repayment schedule provides a detailed timeline for payments, often specifying monthly installments due on a particular date each month, outlining the total loan amount, payment frequency (such as bi-weekly or monthly), and total duration, which might span anywhere from one year to thirty years depending on the loan specifics and lender policies. This contract ensures both parties understand their obligations and provides a framework for financial planning.
Late payment penalties and fees
Late payment penalties can significantly impact the financial obligations outlined in loan repayment contracts. Commonly, a grace period of 15 days after the due date is implemented, allowing borrowers to settle payments without immediate repercussions. Following this period, a late fee may be incurred, typically ranging from 5% to 10% of the outstanding balance, contributing to the principal amount owed. In addition, lenders often impose additional interest charges on late payments, which can accrue monthly. Failure to address late payments may also lead to adverse effects on the borrower's credit score, as reported to credit bureaus such as Experian and TransUnion. Ensuring timely repayment is crucial to avoid these penalties and maintain a good financial standing.
Signatures and legal jurisdiction
A loan repayment contract typically includes essential details regarding the agreement, including parties involved, loan amount, interest rates, payment schedule, and consequences of default. The signatures section signifies acceptance and commitment to the terms outlined, requiring the borrower and lender to provide their legal signatures, which solidify the contract. Legal jurisdiction refers to the specific geographical area or court system that governs any disputes arising from the contract, ensuring that both parties are aware of the legal framework applicable to their agreement, often defined by state or national laws where the loan transaction occurred.










Comments