In today's unpredictable business landscape, having a robust business continuity plan is more essential than ever. This outline will guide you through key components, ensuring that your organization is well-prepared to handle disruptions â be it natural disasters, cyber threats, or any unforeseen events. By prioritizing resilience and proactive strategies, you can safeguard your company's operations and maintain trust with your stakeholders. So, let's dive deeper into the specifics of crafting an effective business continuity plan that works for you!

Executive Summary
The Executive Summary of a Business Continuity Plan (BCP) serves as a high-level overview of the strategies implemented to ensure operational resilience during unexpected disruptions. It should succinctly highlight the organization's core objectives in maintaining essential functions, such as safeguarding key personnel, protecting critical infrastructure, and securing vital information systems during crises. A robust BCP typically draws from recent risk assessments conducted, identifying vulnerabilities and potential threats ranging from natural disasters, cyber-attacks, to pandemics. The outline also incorporates incident response protocols, recovery procedures, and communication plans, detailing roles and responsibilities among team members, with an emphasis on compliance with relevant regulations and standards. Ultimately, the Executive Summary should convey the organization's commitment to minimizing downtime and protecting business interests, fostering a culture of preparedness and proactive risk management.
Risk Assessment and Business Impact Analysis
Risk Assessment identifies potential threats such as natural disasters, cyber-attacks, and equipment failures that could disrupt business operations. Key factors include likelihood (expressed as a percentage), severity (on a scale from 1 to 5), and exposure (the potential financial impact in USD). Business Impact Analysis evaluates critical business functions, including revenue-generating activities, and determines recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPO) for each function. Scenarios may encompass specific incidents, like a server outage in data centers located in Austin, Texas, or a significant supply chain disruption affecting partnerships with manufacturers overseas. This analysis informs resource allocation and response strategies, ensuring organizational resilience during unforeseen events.
Business Continuity Strategies
Business continuity strategies encompass a set of comprehensive procedures aimed at ensuring operational resilience during unexpected disruptions, such as natural disasters, cyber attacks, or equipment failures. Key elements include risk assessment methodologies, which identify vulnerabilities in infrastructure and processes, ensuring a proactive approach to potential threats. Critical function identification establishes priorities for sustaining essential services, particularly in sectors like healthcare facilities, IT services, and manufacturing plants. Resource allocation strategies, including backup systems and alternative sourcing for materials, play a vital role in maintaining operations. Communication plans, detailing internal and external stakeholder notifications, are crucial for effective information dissemination during incidents. Regular training and drills, scheduled quarterly or bi-annually, ensure that employees can respond effectively should a crisis arise. Finally, continuous monitoring and improvement processes, facilitated by periodic reviews, adapt to evolving risks and organizational changes.
Response and Recovery Procedures
Response and recovery procedures are essential components of a business continuity plan that ensure organizational resilience during disruptive events such as natural disasters, cybersecurity incidents, or significant operational failures. These procedures typically outline specific actions that must be taken immediately following an incident, detailing crisis communication protocols, resource allocation, and roles assigned to key personnel to facilitate a swift reaction. A well-structured response framework includes steps for assessing damage, prioritizing recovery efforts based on business impact analysis (BIA), and coordinating with external agencies such as local emergency services or IT support teams. Recovery strategies should aim at restoring critical business functions, ensuring data integrity, and implementing lessons learned for future preparedness. Regular testing and updates of these procedures are crucial to adapt to evolving threats and maintain operational continuity.
Maintenance and Testing Schedule
A well-structured maintenance and testing schedule is essential for ensuring business continuity in the event of disruptions. Regular maintenance tasks, including server inspections, data backups, and security updates, should be conducted on a monthly basis (for example, the first Monday of each month) to prevent system failures. Testing of disaster recovery plans must occur semi-annually, ideally in March and September, to verify procedures, update contact lists, and assess recovery time objectives (RTO). Additionally, annual penetration testing should be scheduled for November to identify vulnerabilities in security systems. Documentation of test results and maintenance activities is crucial, fostering accountability and transparency in the continuity framework.
Letter Template For Business Continuity Plan Outline Samples
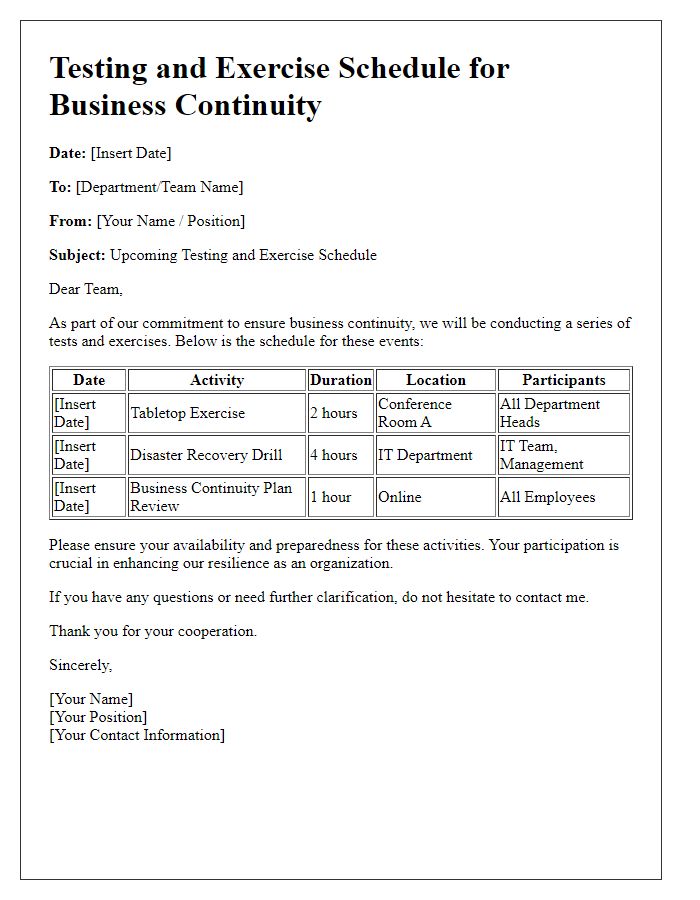
Letter template of Testing and Exercise Schedule for Business Continuity












Comments