Are you looking to streamline your document signing process? A digital signature authorization letter template can save you time and ensure the integrity of your agreements. With just a few clicks, you can provide authorization for your electronic signature, making transactions faster and more efficient. Dive into our article to discover how easy it is to create and use this essential tool!

Clear Subject Line
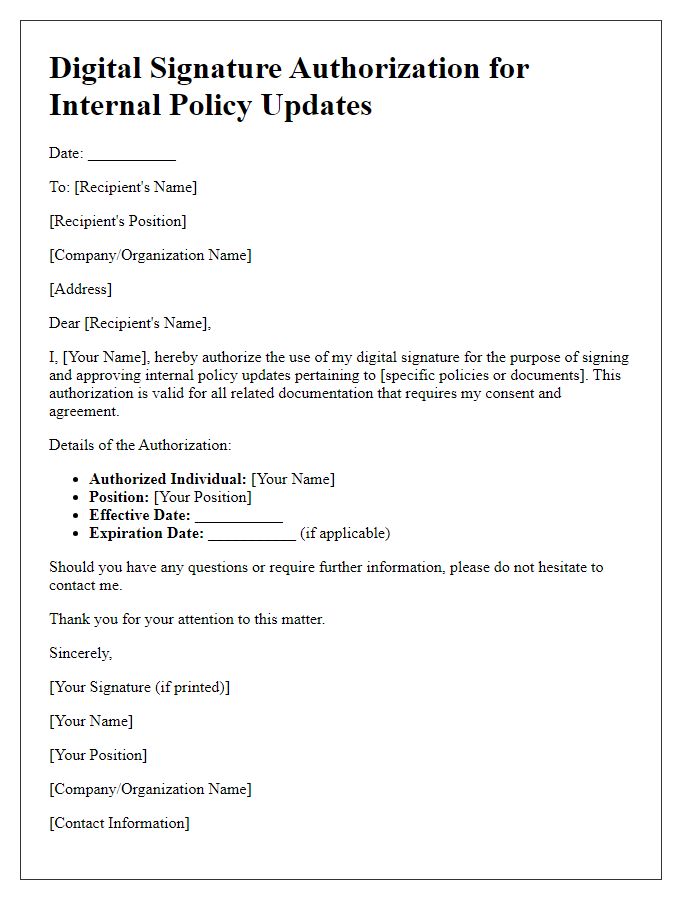
Digital signature authorization refers to the formal process where individuals grant permission for their digital signature to be used on electronic documents. This authorization typically involves terms, conditions, and the specific scope of usage, ensuring that the signer's identity and intent are secured. Such agreements often cover remote transactions, financial contracts, and legal agreements that require signatures. Key entities in such processes include notary services and electronic signature platforms like DocuSign or Adobe Sign, which enhance security through encryption and verification mechanisms. Properly drafted authorization letters help prevent unauthorized access and maintain trust in digital communications.
Date of Authorization
Digital signature authorization is a crucial step in verifying the authenticity of electronic documents. The Date of Authorization marks the specific moment a sender (individual or organization) permits a recipient to use their digital signature, ensuring compliance with legal standards such as the Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act (ESIGN) in the United States or the eIDAS regulation in Europe. This date, formatted typically as MM/DD/YYYY, establishes a time frame for the validity period of the authorization. Accurate documentation of this date enhances legal protections and fosters trust in the signing process. It aligns with best practices for digital transactions and aids in audit trails for future reference.
Authorized Signatory Details
Digital signature authorization enables secure electronic transactions, ensuring authenticity and integrity. An authorized signatory, such as a company executive or legal representative, holds the responsibility of validating documents and agreements electronically. Key details include the signatory's full name, job title, organization name (e.g., Tech Innovations LLC), and contact information. Additional elements may include the date of authorization and any associated digital certificate information. Utilizing digital signatures streamlines processes in various sectors, ranging from finance to legal services, enhancing efficiency and compliance with regulations such as the eIDAS in Europe or the ESIGN Act in the United States.
Specific Purpose of Authorization
Digital signature authorization is critical in various sectors, particularly in legal documents and online transactions. Specific purposes for authorization may include signing contracts, approving financial documents, or validating identity in electronic communications. For instance, an authorized digital signature can ensure the legitimacy of an employment contract, allowing for efficient onboarding without the need for physical presence. In financial environments, lenders may require a digital signature for loan documents, streamlining the application process. Furthermore, regulatory compliance in industries like healthcare often mandates digital signatures for patient consent forms, enhancing security and traceability. The use of secure cryptography in digital signatures protects sensitive data, ensuring that the authorizing party's identity and intent are verifiable and trusted.
Contact Information and Verification Process
Digital signature authorization enables secure online transactions and legal agreements. Users must provide their contact information, including email (ensuring notifications and confirmations), phone number (for verification purposes), and an address (for legal documentation). Verification processes involve identity confirmation, often utilizing government-issued IDs (like driver's licenses or passports) to authenticate individual identities. Digital signature systems rely on Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), which employs unique cryptographic keys to verify signer's authenticity. Additionally, employing two-factor authentication (2FA) enhances security by requiring a secondary confirmation method, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access and execute critical documents.
Letter Template For Digital Signature Authorization Samples
Letter template of digital signature authorization for business contracts

Letter template of digital signature authorization for financial documents

Letter template of digital signature authorization for project approvals

Letter template of digital signature authorization for vendor agreements

Letter template of digital signature authorization for employee onboarding

Letter template of digital signature authorization for software licenses

Letter template of digital signature authorization for corporate communications






Comments