Are you navigating the intricacies of provisional tax payments and feeling a bit overwhelmed? You're not alone! This article breaks down everything you need to know about provisional tax payment advice, simplifying the process in a way that anyone can understand. So, grab a cup of your favorite drink and dive in to discover tips and tricks that will make managing your tax obligations a breeze!

Taxpayer's details
Taxpayer details play a crucial role in the provisional tax payment process, especially for individual and corporate entities. Essential information includes the taxpayer's name, which identifies the individual or business registered with the revenue authority. Tax identification number (TIN) serves as a unique identifier for the taxpayer, crucial for matching tax records and payments. Address, including city, state, and postal code, ensures accurate communication and notification from the tax office. The fiscal year, usually denoted by specific dates, indicates the period for which the provisional tax payment applies. Furthermore, income details reflect the taxpayer's earnings, often subject to taxation, impacting the provisional payment amount required. Also, contact information, including phone number and email address, facilitates timely updates and clarifications regarding tax obligations.
Tax period and due date
Provisional tax payment advice informs taxpayers about the required payment amounts and deadlines for their estimated tax liabilities. The tax period, usually a 12-month fiscal year for individuals and businesses, culminates in significant deadlines that vary by jurisdiction. Depending on local regulations, due dates may occur biannually (in some cases, mid-August and mid-January) or quarterly. Missing these deadlines can lead to penalties, interest charges, or additional tax assessments. Taxpayers must stay organized and aware of their financial obligations to avoid complications during tax filing seasons and ensure compliance with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) or equivalent authorities.
Calculation method and payment summary
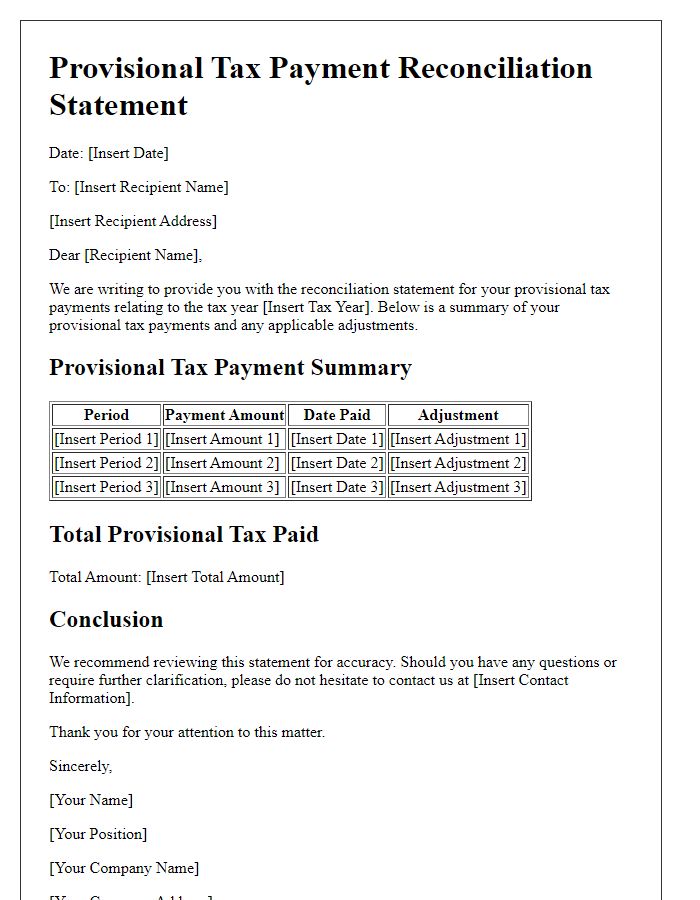
Provisional tax payment advice includes essential elements such as the calculation method used to determine tax liabilities and a detailed payment summary. The calculation method typically relies on the estimated annual income figure, which is calculated based on previous year's income or adjusted for anticipated changes, like income growth or business expansion. For example, if last year's income was $80,000, the provisional tax for the current year might be calculated at 90% of this amount, resulting in a tax obligation of $72,000. Payment summaries should reflect any advance payments made, the total provisional tax owed, and specific due dates. Important dates like the first payment deadline often fall in July, with subsequent payments due in January and May, aligning with tax year cycles. Clients should also retain forms such as the IR 100 to ensure compliance with local regulations.
Payment instructions and options
Provisional tax payments require clear instructions to ensure compliance and timeliness. Taxpayers must adhere to specific deadlines set by tax authorities, typically occurring twice a year, with the first payment due within six months of the fiscal year-end in many countries. Payment options include bank transfers, utilizing reference numbers provided by tax offices, or online payment portals designed for the respective tax agency. For example, individuals in South Africa must adhere to the dates prescribed by the South African Revenue Service (SARS) and must ensure their payments reference the correct unique taxpayer number (UTN). Deadlines are critical; payments made after specified dates incur interest and penalties, complicating tax obligations. Ensuring the correct amount--often calculated based on estimated annual income--further aids in compliance and avoidance of future issues.
Contact information for inquiries
Provisional tax payment advice is crucial for taxpayers in jurisdictions requiring estimated tax payments throughout the year, commonly observed in systems like those in South Africa or Australia. These payments are typically based on expected income, helping individuals and businesses avoid penalties associated with underpayment. Taxpayers should take note of critical dates, often falling on February 28 and August 31 in South Africa, for submission to the South African Revenue Service (SARS). For inquiries related to these provisional tax payments, it is essential to have access to customer service contact details, typically available on official government tax websites. These resources provide guidance for taxpayers navigating payment processes, ensuring compliance and timely submission of required amounts.










Comments