When it comes to ensuring the quality of raw materials, a thorough and systematic approach is vital for any production process. Whether you're a seasoned professional or new to the industry, understanding how to effectively check and document the quality of your raw materials can significantly impact your end product's success. In this article, we'll guide you through a comprehensive letter template designed for conducting quality checks, ensuring that you communicate clearly and effectively with your suppliers. So, let's dive in and explore how this simple tool can enhance your quality assurance practices!

Purpose and Intent of the Quality Check
Raw material quality checks serve as a crucial quality assurance measure in manufacturing sectors, including automotive and pharmaceuticals. These checks aim to ensure that raw materials, such as polymers, metals, and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), meet specified standards and specifications outlined by industry regulations. The quality check process involves rigorous testing methodologies, such as spectrometric analysis and tensile strength evaluations, to assess the physical and chemical properties of the materials. Establishing compliance with standards set by organizations like ISO (International Organization for Standardization) ensures that the final products maintain safety and efficacy, reducing potential risks associated with product recalls or batch failures during production. Regular audits and sampling techniques contribute to maintaining material integrity, ultimately supporting the overall reliability and performance of manufactured goods.
Detailed Description of the Raw Materials
Raw materials quality checks are crucial for maintaining production standards in industries such as pharmaceuticals and construction. It includes evaluating metals like aluminum and steel, which should meet specifications such as ASTM standards for strength and corrosion resistance. In the case of pharmaceuticals, raw materials must adhere to the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) guidelines for purity and potency. The quality inspection process may involve testing samples for chemical composition, physical properties, and moisture content, with acceptable parameters defined by industry standards or internal benchmarks. Documentation of quality checks must be maintained rigorously, including batch numbers, supplier information, and test results to ensure traceability and compliance with regulations, such as those set forth by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Specific Quality Standards and Requirements
The raw material quality check process ensures compliance with specific quality standards outlined by organizations such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) and ISO (International Organization for Standardization). Materials must meet precise specifications including composition, physical properties, and performance criteria, evaluated through rigorous testing methods. For example, steel grades subjected to tensile strength tests may need to achieve a minimum yield strength of 350 MPa. Suppliers should provide documentation including certificates of analysis (CoA) that detail the results particularly focusing on chemical composition and contamination levels under accepted thresholds. This systematic approach ensures that materials sourced for industrial applications consistently meet performance and safety requirements, thereby reducing the risk of production delays and failures in final products.
Inspection Procedure and Methodology
The inspection procedure and methodology for raw material quality checks are crucial in ensuring that materials conform to specified standards. This process typically entails visual inspections to identify physical defects, such as cracks or foreign particles, in materials like metals or plastics sourced from suppliers. Additionally, quantitative assessments involve measurements of tensile strength, hardness, and chemical composition, usually through methods such as tensile testing per ASTM D638 norms. Calibration of measuring equipment, including hardness testers and micrometers, is mandatory to guarantee precise readings. Sampling plans, often following military specifications (MIL-STD-105E), dictate the number of samples taken for batch testing, ensuring statistical relevance. Documentation of results must be meticulously recorded and analyzed to maintain traceability and reliability of the materials used in manufacturing processes across industries, including automotive and aerospace sectors.
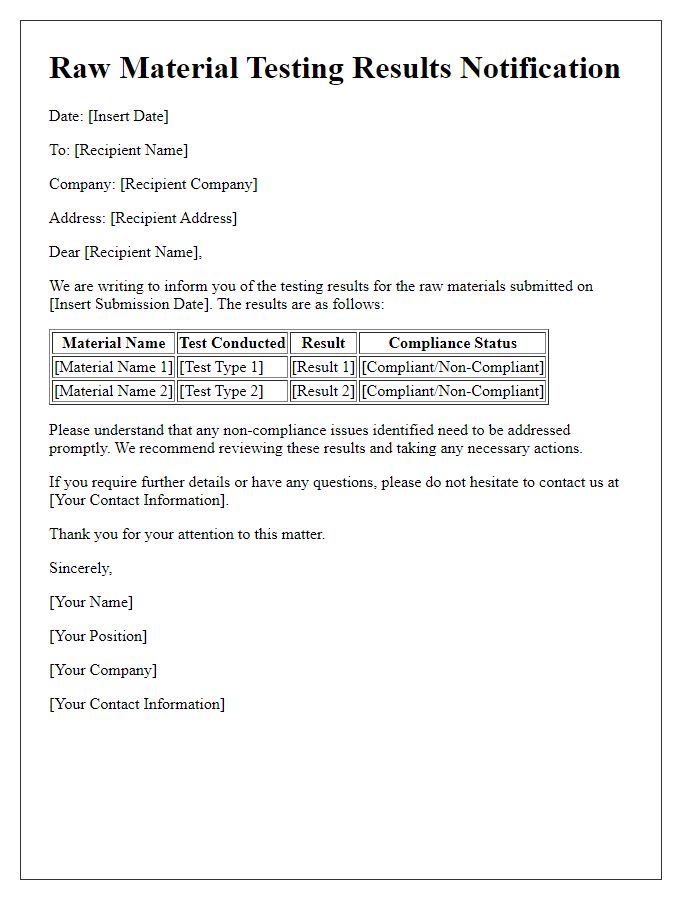
Reporting and Communication Protocols
Raw material quality checks serve as a critical process for ensuring the integrity of production in various industries, including manufacturing and pharmaceuticals. Quality assurance protocols dictate that samples of incoming materials, such as polymers, metals, or active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), undergo rigorous testing in accredited laboratories. Reports generated highlight parameters such as purity levels, structural integrity, and compliance with industry standards, including ISO 9001. Communication protocols mandate timely reporting of findings to relevant stakeholders, ensuring swift resolution of identified issues, such as non-conformance or contamination. Effective documentation practices preserve a traceable history of material quality assessments, crucial for audits by regulatory bodies like the FDA or EPA, thereby reinforcing the overall compliance framework for industries committed to maintaining product excellence.












Comments