Welcome to our guide on creating an essential IT resources checklist for your office! Having the right tools and technology in place can greatly enhance productivity and streamline processes. In this article, we'll cover everything from hardware requirements to software essentials, ensuring your team is well-equipped to tackle any challenge. Curious about what to include in your checklist? Let's dive in!

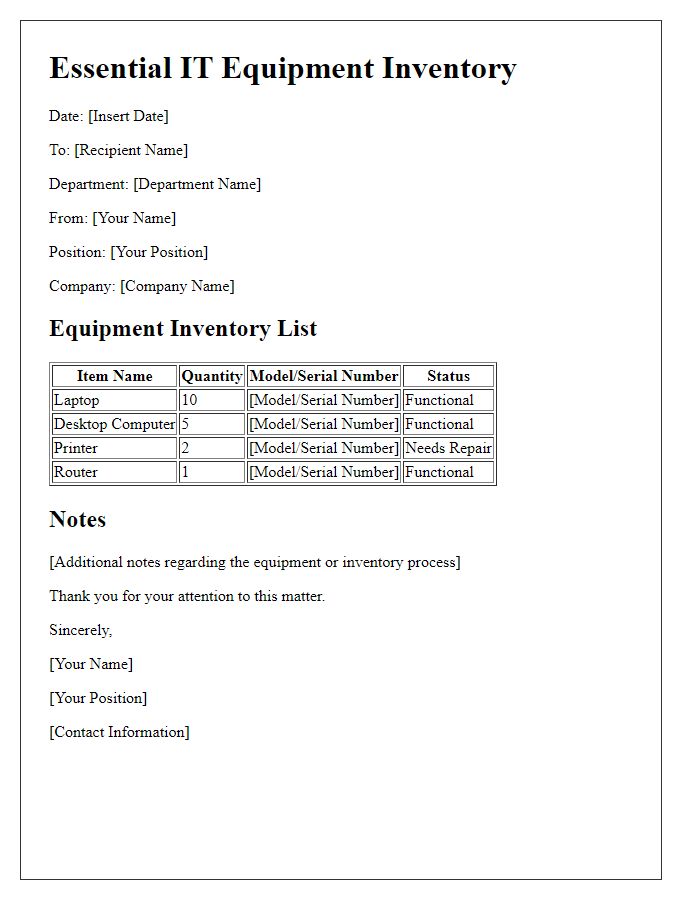
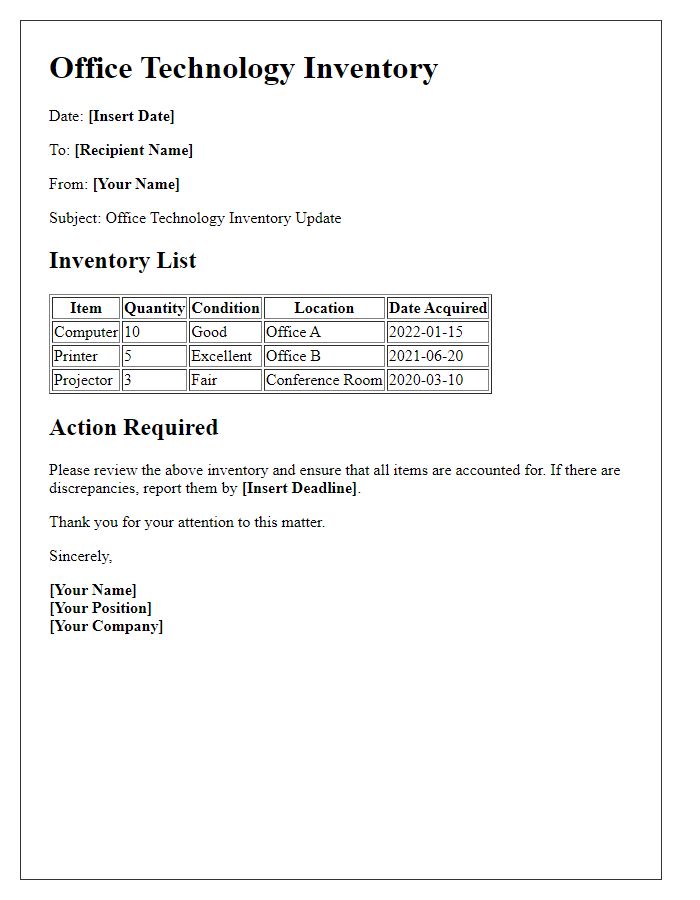
Comprehensive Asset Inventory
A comprehensive asset inventory for office IT resources includes critical components such as computers, servers, and networking equipment. Each device, for instance, laptops from brands like Dell or HP, should be documented with specifications including processor type, memory size (e.g., 16GB RAM), and storage capacity (e.g., 512GB SSD). Software licenses must also be logged, detailing applications like Microsoft Office (with version numbers) and antivirus programs to ensure compliance and security. Additionally, peripheral devices like printers (e.g., HP LaserJet Model) and monitors (with specifications like display size or resolution) play a vital role in the workflow. Tracking accessories such as keyboards and mice along with their condition status can enhance maintenance planning. Maintaining this inventory at a centralized database facilitates efficient resource allocation and management.
Software Licensing Compliance
Software licensing compliance is crucial for organizations to avoid legal repercussions and maintain operational integrity. A comprehensive checklist can help ensure adherence to licensing agreements for software products such as Microsoft Office, Adobe Creative Cloud, and antivirus programs like Norton or McAfee. Key elements of compliance include verifying the number of licenses compared to the number of installed software instances, documenting any usage limits, and ensuring all software is updated to prevent security vulnerabilities. Regular audits, ideally conducted quarterly, should assess the installation status on all devices and confirm that licenses are stored securely, accessible only to authorized personnel. Additionally, awareness programs can educate employees on the importance of compliance to foster a culture of responsibility.
Network Security Measures
In the realm of network security measures, organizations must prioritize a robust firewall system, essential for monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. This foundational layer can prevent unauthorized access and threats. Moreover, implementing a Virtual Private Network (VPN) safeguards sensitive data, especially for remote workers or during in-transit data transfer. Regular updates of antivirus software and intrusion detection systems enhance protection against malware, ransomware, and cyber attacks, which have surged by 300% globally from 2019 to 2021. Access controls are vital, establishing role-based permissions to sensitive data restricted only to authorized personnel. Routine security audits, as mandated by compliance regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA, are necessary to identify vulnerabilities and address potential breaches. Employee training on phishing awareness ensures that staff recognize and mitigate risks associated with social engineering attacks. Additionally, multi-factor authentication (MFA) improves account security by requiring multiple forms of verification, significantly reducing the likelihood of unauthorized access. Collaborative efforts between IT teams and management are crucial in maintaining an adaptable, secure network environment against evolving threats.
Hardware Lifecycle Management
Effective hardware lifecycle management is essential for maintaining optimal performance and efficiency in office IT resources, such as computers, servers, and networking equipment. Regular assessments of hardware inventory, including CPU specifications and storage capacities, help identify devices nearing obsolescence, typically after three to five years of usage. Monitoring manufacturer support and warranty status is crucial for ensuring prompt repairs and replacements. Additionally, maintaining a detailed record of upgrades, including firmware updates and installed software versions, prevents compatibility issues. Implementing a secure data sanitization process before disposing of outdated hardware ensures compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR. Regular reviews and updates to the IT resources checklist facilitate proactive planning for hardware purchases and replacements, aligning with emerging technology trends.
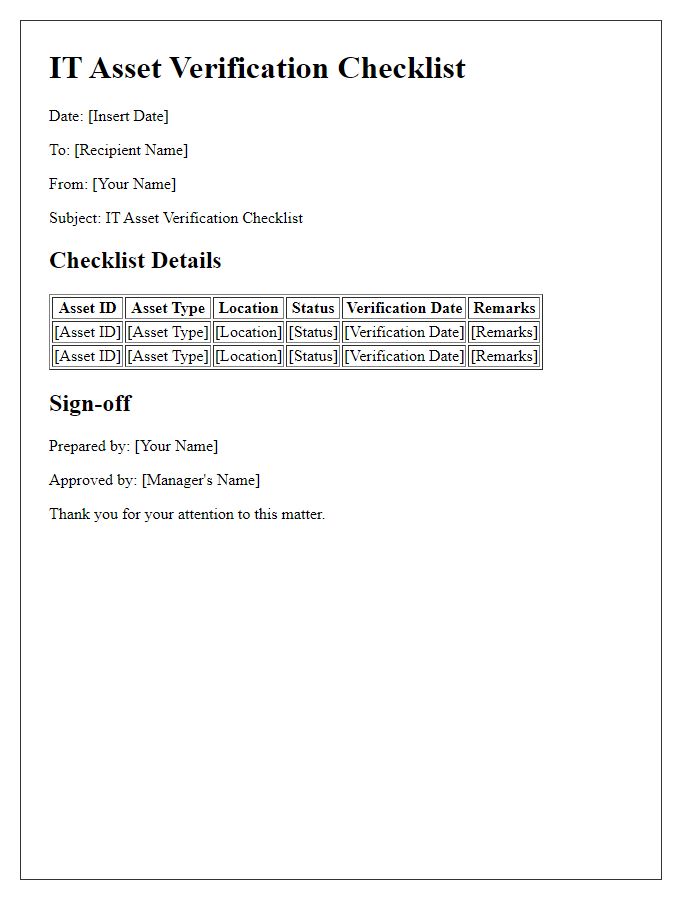
User Access and Permissions Control
User access and permissions control is essential for maintaining security and efficiency within office IT environments. Each user account must be assigned appropriate access levels to sensitive data and applications, following the principle of least privilege. The checklist should include critical items such as user roles and responsibilities, account creation procedures, access rights reviews (ideally conducted quarterly), and the use of multi-factor authentication to strengthen security layers. Administrators should regularly audit user permissions using monitoring tools, ensuring compliance with internal policy standards and industry regulations like GDPR or HIPAA. Logging access attempts and changes to permissions is vital for tracking unauthorized access and responding to potential security breaches effectively.









Comments