Hey there! We all know that managing medication can sometimes feel like navigating a complex maze, and that's why staying informed is so important. Whether it's a dosage change or a new prescription, understanding these updates can make a significant difference in your health journey. If you're curious about how to handle medication adjustments effectively, keep reading for valuable insights and tips tailored just for you!

Patient Information
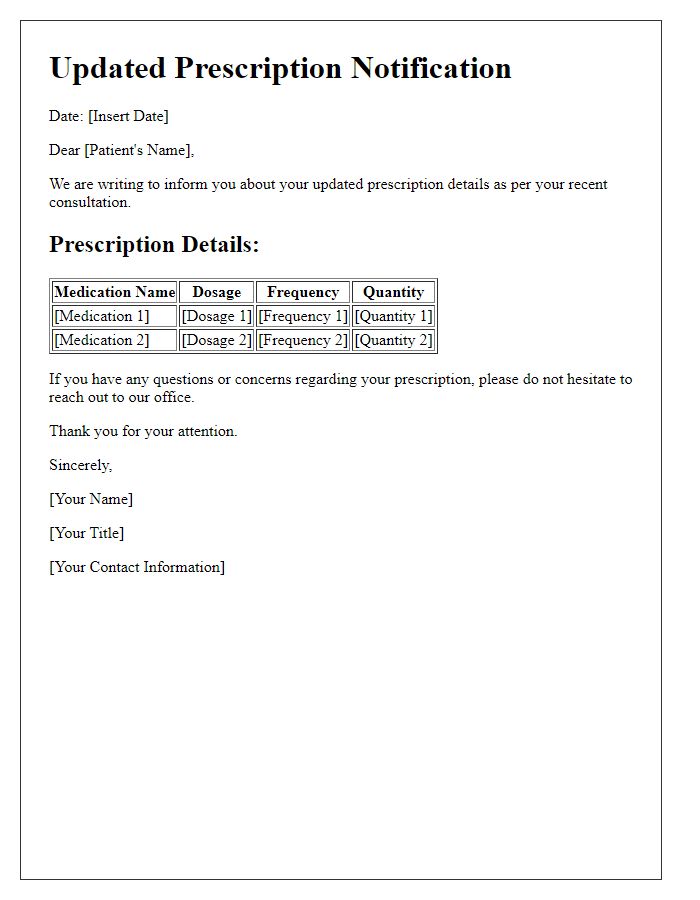
Medication adjustment notifications are crucial for patient safety and care continuity. Proper documentation must include patient information such as full name, date of birth (typically in a MM/DD/YYYY format), and unique medical identification number. The specific medication name, dosage, and the reason for adjustment should be clearly outlined, along with the scheduled date for the new dosage to take effect. Additionally, healthcare provider contact information, including office phone number and email address, is essential for follow-up questions. Clear instructions regarding potential side effects and when to seek assistance can enhance patient understanding and compliance.
Medication Details
Medication adjustment notifications are crucial for ensuring patient safety and optimal therapeutic outcomes. Medications, such as anticoagulants or antidepressants, require precise dosing, as alterations can lead to significant health implications. For instance, warfarin, commonly prescribed for preventing blood clots, necessitates meticulous INR (International Normalized Ratio) monitoring to avoid bleeding complications or thrombotic events. Communication regarding changes should include details such as dosage adjustments, frequency alterations, and potential side effects. Consistent updates from healthcare providers ensure patient adherence and understanding, ultimately contributing to effective disease management and improved quality of life.
Adjustment Reason
Medication adjustments are often necessary to enhance treatment efficacy or mitigate side effects. For instance, a physician may lower the dosage of an antihypertensive medication like Lisinopril due to persistently low blood pressure readings, typically below 90/60 mmHg. Conversely, increasing the dosage of insulin might be warranted if blood glucose levels, as indicated by home monitoring logs, consistently exceed 180 mg/dL after meals. Adjustments can also arise from laboratory results; for example, a patient's electrolyte levels may necessitate a reduction in diuretic use. Each modification aims to optimize patient outcomes, aligning with clinical guidelines and individual health conditions.
Dosage Instructions
Dosage adjustments for medications are crucial for effective treatment in chronic conditions like hypertension or diabetes. Proper dosage information, such as milligrams per day, must be communicated clearly to prevent complications. For example, abrupt changes in dosage might lead to blood sugar fluctuations in diabetic patients, while inaccurate blood pressure medication dosages could result in severe hypertension or hypotension. Specific medications, like Metformin or Lisinopril, often require gradual adjustments based on patient response and lab results, such as hemoglobin A1c or blood pressure readings, to ensure optimal therapeutic outcomes. Regular monitoring and communication with healthcare providers are essential to ensure safety and efficacy in medication management.
Healthcare Provider Contact Information
Healthcare providers must notify patients regarding medication adjustments, emphasizing changes in dosages, side effects, and new prescriptions. For instance, a healthcare provider may contact a patient regarding the adjustment of an antidepressant, such as Sertraline, which requires careful monitoring. Health professionals should include their contact information, including the clinic's name, address in Chicago, Illinois, direct phone numbers, and emergency contact hours. Additionally, providing clear instructions on follow-up appointments and potential side effects, like nausea and insomnia, is essential to ensure proper patient understanding and adherence to the adjusted medication regimen.












Comments