Are you looking to take charge of your kidney health? Staying on top of your kidney health monitoring schedule is crucial for early detection and management of any potential issues. With simple steps and regular check-ups, you can significantly improve your kidney function and overall well-being. Join us as we dive into effective strategies and tips for maintaining optimal kidney healthâread on to discover more!

Personalized Patient Information
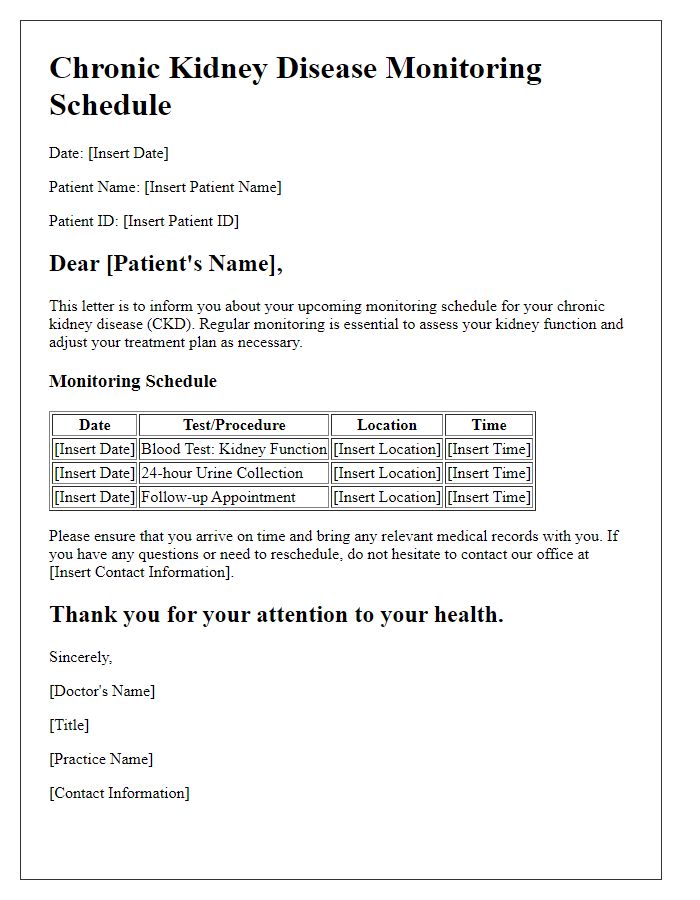
Routine kidney health monitoring is essential for patients diagnosed with chronic kidney disease (CKD) or those at risk. The monitoring schedule includes regular assessments of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) using blood tests, ideally every three months, alongside urine tests to measure protein levels indicative of kidney damage. Blood pressure readings, targeting below 130/80 mmHg, are crucial at each visit to mitigate further kidney deterioration. Additionally, consultation appointments should include discussions regarding lifestyle modifications, such as dietary restrictions on sodium and phosphorus, and adherence to prescribed medications, including ACE inhibitors or ARBs which play a significant role in kidney protection. Educational resources should also be provided to emphasize the importance of fluid intake and maintaining a healthy weight in managing overall kidney health. Regular communication with healthcare providers at nephrology clinics in local hospitals, such as County General Hospital, enhances patient understanding and improves outcomes through tailored health strategies.
Purpose of Monitoring
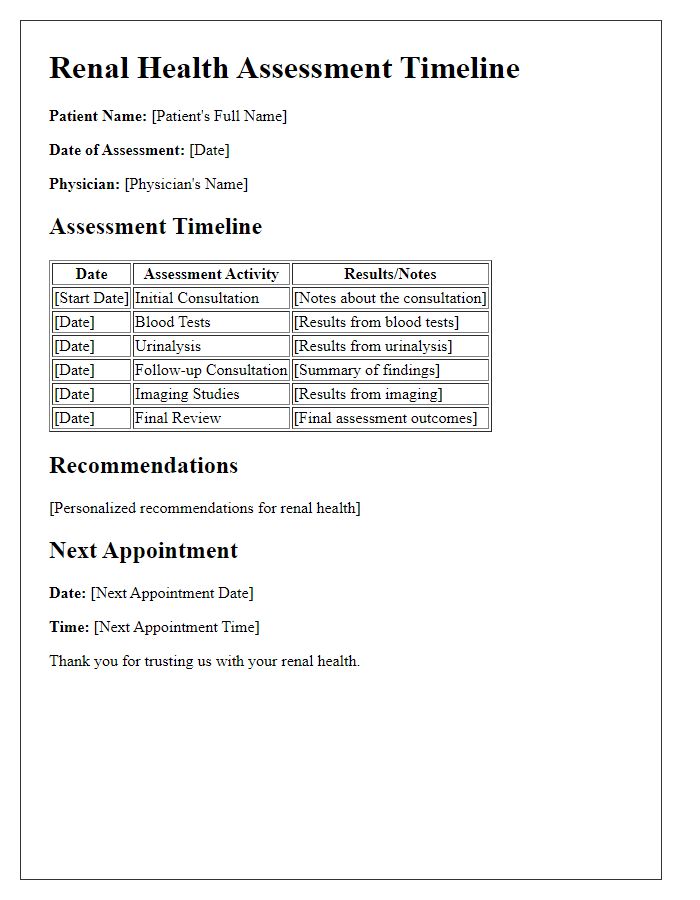
Regular kidney health monitoring is essential for individuals at risk of chronic kidney disease (CKD), including those with diabetes and hypertension. Kidney function tests, such as serum creatinine and glomerular filtration rate (GFR), provide critical insights into the organ's performance, assessing filtration efficiency and waste elimination. Monitoring also helps detect electrolyte imbalances, such as elevated potassium levels (hyperkalemia), which can be life-threatening. Routine examinations should include urinalysis to identify proteinuria, an early sign of kidney damage. Engaging in a structured schedule allows timely interventions, such as medication adjustments and lifestyle modifications, promoting overall kidney health. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers, ideally at least twice a year, ensure comprehensive management of kidney health and prevention of progression to more severe stages of CKD.
Scheduled Dates and Times
Kidney health monitoring plays a crucial role in managing chronic conditions such as diabetes and hypertension. Regular check-ups, typically scheduled every three months, involve blood tests to measure creatinine levels (normal range 0.6 to 1.2 mg/dL for adults) and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) assessments to evaluate kidney function. Urinalysis is another essential test to detect protein or blood (indicators of potential kidney damage) in urine. Patients may also be advised to follow a specific diet, rich in fruits and vegetables, while limiting sodium intake to enhance kidney function. Additionally, keeping track of blood pressure readings (target levels below 130/80 mmHg) and monitoring weight can help in assessing overall kidney health. It's essential to maintain a detailed schedule of these monitoring dates and times, ensuring all necessary tests are conducted timely for effective health management.
Preparation Instructions
Effective kidney health monitoring necessitates a well-structured schedule for optimal preparation. Individuals should begin with early morning urine collection to assess biomarkers such as creatinine and albumin, crucial for evaluating kidney function. Ensure hydration levels are adequate, aiming for at least two liters of water daily, as hydration profoundly influences test results. Prior to testing, fasting may be required for a minimum of eight hours to ensure accurate blood glucose and electrolyte readings. Monitor blood pressure at home using a validated monitor to provide additional data points; maintain a log of readings. Note medication timings since certain medications can affect renal parameters. Lastly, consult healthcare providers regarding any dietary restrictions or lifestyle changes, particularly with sodium intake and potassium-rich foods, which can significantly impact kidney health.
Contact Information for Inquiries
Kidney health monitoring schedules are crucial for individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD) or those at risk. Regular assessments include blood tests measuring creatinine levels, urine tests evaluating protein levels, and blood pressure evaluations, ensuring early detection of potential complications. Patients should maintain updated contact information for healthcare providers, facilitating inquiries about test results, medication adjustments, or lifestyle recommendations. Local nephrology clinics, like the Kidney Care Center in Houston, Texas, offer resources and support for managing kidney health. Establishing a personalized schedule, outlining test frequency--typically every three to six months--empowers patients to take proactive steps in their kidney health journey.










Comments