Are you looking to secure funding for rural healthcare initiatives? Writing a compelling letter can make all the difference in showcasing the urgent need for support in underserved communities. In this article, we'll explore effective strategies and templates that can help you craft an impactful grant letter tailored for rural healthcare needs. Join us as we delve deeper into the essentials to enhance your grant application!

Needs Assessment
Rural healthcare facilities often face significant challenges, including limited access to medical services, a shortage of healthcare professionals, and inadequate funding. Communities such as those in rural Appalachia and the Northern Great Plains (which are home to many underserved populations) struggle with higher rates of chronic diseases like diabetes and hypertension, impacting overall health outcomes. For instance, data from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services indicates that rural residents visit physicians 20% less frequently than their urban counterparts. This underutilization, compounded by transportation barriers to reach healthcare centers (distance often exceeding 30 miles in some areas), exacerbates health disparities. Furthermore, many rural facilities operate with inadequate resources, leading to reduced capacity for essential services like emergency care, preventative screenings, and mental health support. A comprehensive needs assessment will identify specific healthcare gaps, target populations in need, and prioritize interventions that address these unique challenges, ultimately aiming to strengthen rural health systems and improve access to quality care.
Program Objectives
The rural healthcare grant program aims to improve health outcomes in underserved communities across the United States, specifically targeting areas with limited access to medical resources and specialist care. Objectives include increasing the availability of primary care services by establishing telehealth initiatives, enhancing mental health support systems through community-based programs, and fostering partnerships with local organizations to provide education on preventative care. The program also seeks to reduce health disparities by promoting culturally competent care tailored to the diverse populations in rural regions, ultimately striving to create sustainable health improvements for residents in these challenging healthcare landscapes.
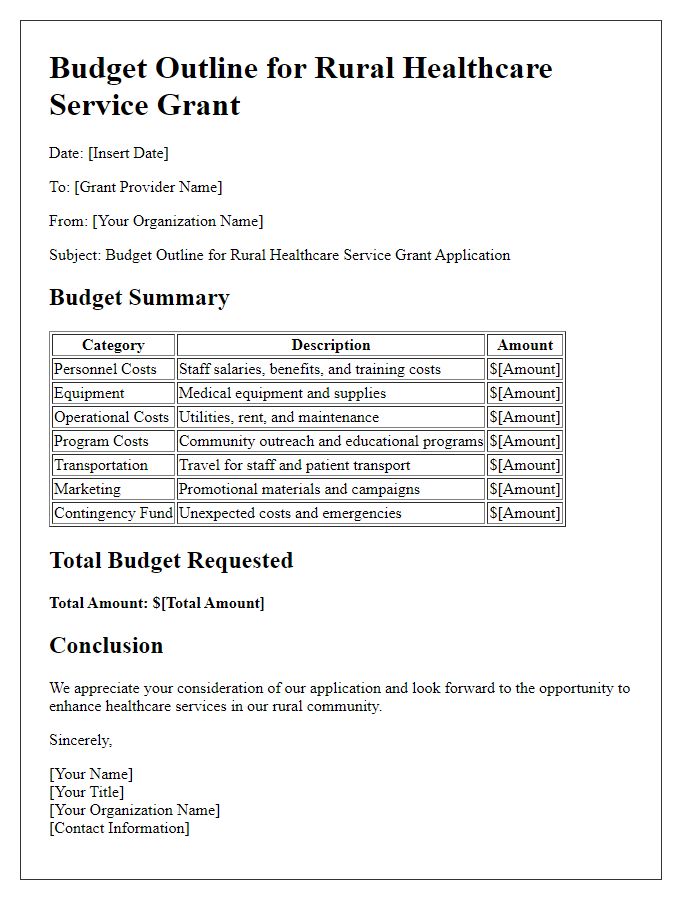
Budget Justification
Rural healthcare grant applications require a well-structured budget justification to ensure proper allocation of funds aimed at improving medical services in underserved areas. The budget includes specific line items such as personnel costs, which encompass salaries for healthcare providers (e.g., doctors and nurses) based on average rural salaries (approximately 15% lower than urban areas). Operating expenses must account for essential supplies, including diagnostic tools (like blood pressure monitors costing around $50 each) and medical equipment, with projections adjusted for rural procurement challenges. Facility renovation expenses should reflect local construction costs, estimated at $150 per square foot for clinics, needed to meet regulatory standards. Additionally, community outreach programs must budget funds for transportation resources, as rural patients often travel over 50 miles to access services. It's critical to outline the expected outcomes tied to each financial request, demonstrating the direct impact on patient care (like reducing hospital readmission rates by 20% over five years).
Evaluation Plan
An effective evaluation plan for a rural healthcare grant should encompass quantitative and qualitative metrics to assess the program's impact on community health outcomes. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as patient engagement rates, treatment adherence statistics, and changes in chronic disease management should be collected from local healthcare facilities. Additionally, demographic data (age, income levels, and geographic location) will provide insight into the target population's health needs. Regular feedback from stakeholders, including healthcare providers, patients, and community leaders, can be gathered through surveys and focus groups. Analyzing healthcare access improvement, particularly in underserved areas like rural Appalachia and the Midwest, will help determine the effectiveness of the implemented strategies. Ongoing data monitoring will facilitate adjustments throughout the program, ensuring sustainable health benefits for the community.
Community Impact
The rural healthcare landscape, encompassing areas like Appalachia and the Great Plains, faces significant challenges in accessibility and quality of care. Statistics reveal that approximately 20% of the U.S. population resides in rural regions, yet these areas have only about 10% of the nation's physicians. Limited access to medical facilities, such as hospitals and clinics, often leads to delayed treatments and poorer health outcomes. For instance, patients in counties with fewer healthcare providers experience an average of 30% longer wait times for appointments, exacerbating chronic health conditions like diabetes and heart disease. Community health initiatives, particularly in the neighborhoods surrounding towns like Marlow, Oklahoma or Woodsville, New Hampshire, focus on improving preventive care through mobile clinics and telehealth services. By addressing healthcare disparities, these programs can significantly enhance health literacy and promote healthier lifestyles among residents, ultimately leading to a decline in preventable diseases and emergency room visits.
Letter Template For Rural Healthcare Grant Samples
Letter template of funding appeal for enhancing rural healthcare services

Letter template of partnership proposal for rural health grant collaboration











Comments