Hey there! Keeping track of your medications can be a daunting task, but updating your medication list doesn't have to be. It's essential for your health and safety to have an accurate record of what you're taking, as it helps avoid potential interactions and ensures your healthcare team is on the same page. Curious about how to easily create and maintain your medication list? Let's dive in!

Patient Information and Identification
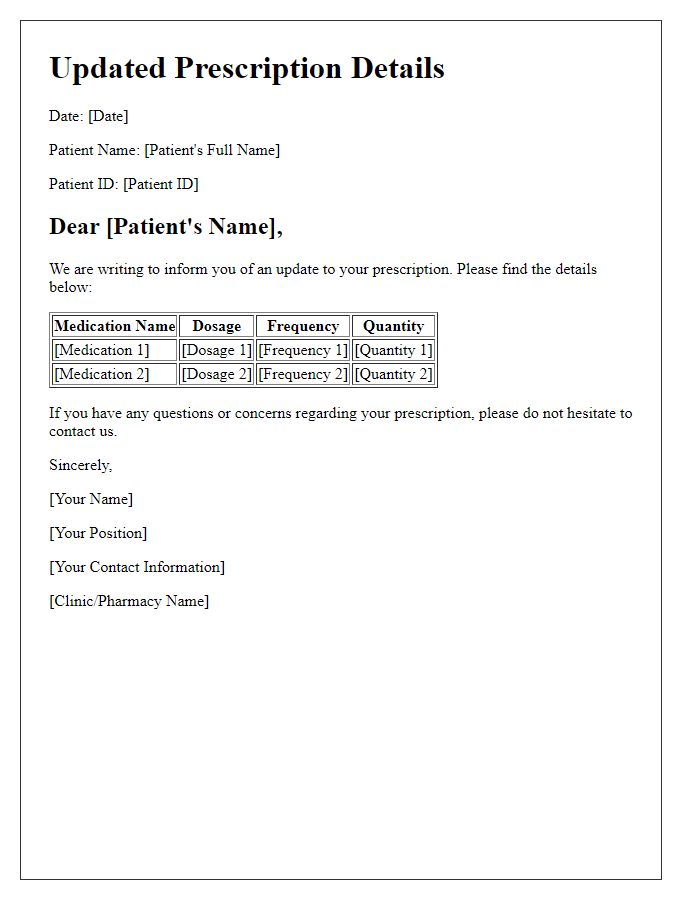
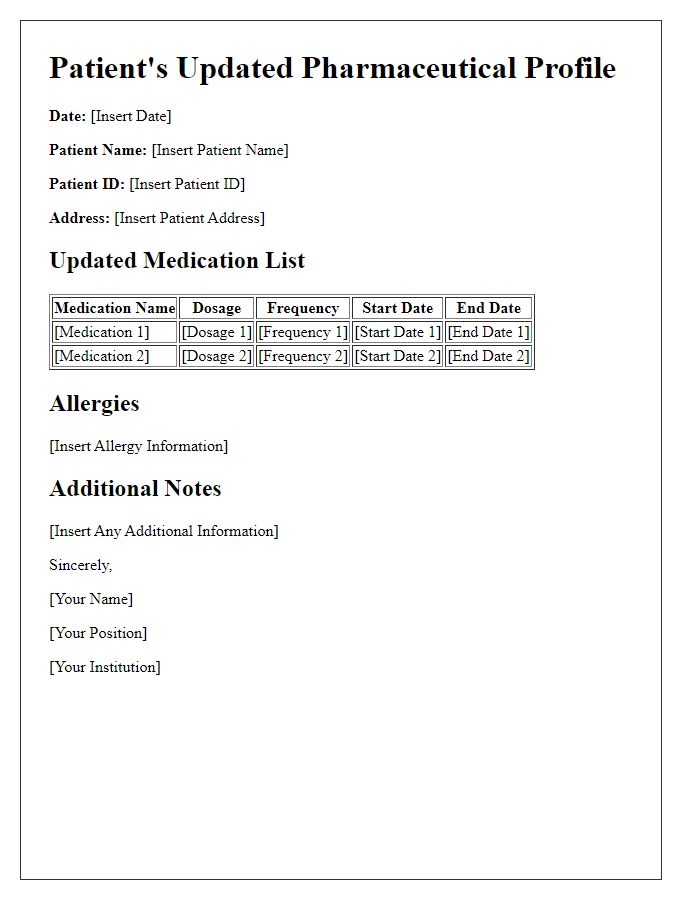
Updated patient medication lists are crucial for ensuring efficient healthcare management. Each patient profile should include essential identification details, such as full name, date of birth, and unique medical record number specific to the healthcare facility. Additionally, comprehensive medication information is necessary, including the generic name and brand name of prescriptions, dosage (in milligrams or other relevant units), frequency of administration (such as twice daily or as needed), and indications for each medication, whether for hypertension, diabetes, or chronic pain management. Regular updates ensure accuracy and prevent adverse drug interactions, particularly for patients with complex medication regimens.
Comprehensive Medication List
A comprehensive medication list is essential for patients to track their prescribed medications, dosages, and schedules accurately. This list includes key details such as the name of each medication, often including common brand names like Lipitor for atorvastatin, along with specific dosages like 20 mg per day. It is crucial to note any over-the-counter medications, herbal supplements, and any past prescriptions that may impact current treatments, such as blood thinners like warfarin. Additional information such as the prescribing physician's name, pharmacy contact details, and refill dates contribute to an organized approach in managing health conditions effectively. Updated medication lists ensure patients and healthcare providers maintain proper communication, reducing the risk of drug interactions and supporting improved health outcomes.
Dosage and Administration Instructions
Updating a patient's medication list requires meticulous attention to detail, especially regarding Dosage and Administration Instructions for pharmaceuticals. For instance, the anticoagulant Warfarin is prescribed at a dosage range of 2 mg to 10 mg, depending on INR (International Normalized Ratio) levels, with specific administration instructions to take it at the same time each day to maintain stable blood levels. It is crucial to indicate whether the patient should take medications with food (e.g., Metformin) or alongside water (e.g., certain antibiotics like Amoxicillin), as these factors can significantly impact absorption and efficacy. Additionally, noting specific frequencies (such as TID - three times daily, BID - twice daily, or QD - once daily) and any other critical instructions, such as avoiding alcohol or other drug interactions (e.g., grapefruit with Statins), would enhance patient safety and compliance in the therapeutic regimen.
Prescribing Physician and Contact Details
An updated medication list is essential for patient safety and effective treatment outcomes. Accurate information regarding prescribed medications, including dosages and schedules, ensures that healthcare providers manage patient care effectively. Key components of this list include the prescribing physician's full name, designation (such as MD or DO), practice details, and contact information, including phone number and email address. This information is crucial for other healthcare professionals who may need to reach out for clarifications or medical decisions. Timely updates to the medication list, particularly during transitions of care or following physician visits, can significantly reduce the risk of drug interactions and enhance overall patient health management.
Revised Date and Signature Verification
Updating a patient's medication list is a crucial task for ensuring safe and effective treatment, particularly for individuals managing chronic conditions. This update process is usually conducted during routine clinical visits or when significant changes occur in therapy. Accurate records must include the revised date, reflecting the most recent evaluation, and a signature verification from a healthcare provider, confirming prescribed medications such as antihypertensives or anticoagulants. Adequate documentation supports patient safety, accountability, and compliance with healthcare regulations, maintaining a clear tracking system for various medications, dosages, and administration routes. Regular reviews, with attention to possible drug interactions, allergies, or contraindications, enhance treatment outcomes and patient education.











Comments