Are you looking to keep your machinery running smoothly and efficiently? Developing a solid maintenance plan is essential for preventing costly downtimes and extending the lifespan of your equipment. In this article, we'll walk you through a comprehensive letter template that can help you outline your machinery maintenance strategy with clarity and precision. So, let's dive in and discover the best practices for effective maintenance planning!

Introduction and Purpose
An effective machinery maintenance plan serves as a critical framework for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of industrial equipment. This plan aims to minimize unexpected downtime and enhance overall productivity by outlining a structured schedule for routine checks, repairs, and preventive measures. By detailing specific maintenance tasks for various machinery types, such as hydraulic presses or conveyor systems, and assigning qualified personnel responsible for these tasks, the plan ensures compliance with safety standards and operational efficiency. Regular maintenance activities, including lubrication, calibration, and parts replacement, are essential to prevent costly failures and extend the lifespan of crucial assets. Ultimately, this maintenance strategy underlines the commitment to maintaining peak operational conditions and supporting the overall goals of the organization.
Scope of Maintenance Activities
A comprehensive machinery maintenance plan encompasses critical activities to ensure optimal performance and longevity of equipment such as hydraulic presses and conveyor belts. Scheduled inspections are vital, assessing key components like bearings and motors every quarter to detect wear and prevent breakdowns. Lubrication practices involve applying the appropriate grease types at specified intervals, typically every 500 operational hours, essential for reducing friction and avoiding overheating. Corrective actions prompt immediate response to malfunctions, ensuring equipment like industrial boilers are repaired within 48 hours to minimize downtime. Additionally, the plan includes training sessions for personnel on best practices in safety measures while operating machinery, reinforcing compliance with OSHA standards. Regular documentation of maintenance activities aids in tracking equipment performance and predicting future needs based on historical data.
Schedule and Frequency
A machinery maintenance plan outlines critical schedules and frequencies vital for optimal equipment performance in industrial settings. Preventive maintenance activities, which include routine inspections, lubrication, and part replacements, often occur bi-weekly or monthly, depending on machinery type, like hydraulic presses or conveyor belts. Annual maintenance typically involves thorough assessments, such as calibration and replacement of wear components, like bearings and seals, ensuring compliance with safety regulations established by organizations like OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration). Additionally, unplanned maintenance, prompted by machinery failures or operational anomalies, requires an expedited response procedure to minimize downtime and production loss, often involving services from specialized technicians or original equipment manufacturers (OEMs).
Roles and Responsibilities
A comprehensive machinery maintenance plan defines specific roles and responsibilities to ensure optimal performance and reliability of equipment, including critical components such as motors, belts, hydraulic systems, and control panels. The Maintenance Manager oversees the entire process, coordinating scheduled maintenance activities, ensuring availability of necessary spare parts, and addressing any emerging issues promptly. Technicians conduct routine inspections, monitoring wear and tear on machinery parts, recording performance data, and executing repairs on equipment, particularly focusing on safety mechanisms and lubrication systems. Operators hold the responsibility for daily checks, implementing operational best practices, and reporting abnormalities in machine performance, which includes vibrations or unusual noises. Additionally, training programs are organized to enhance skills and knowledge, fostering a culture of safety and efficiency among all personnel involved in the maintenance process.
Safety and Compliance Standards
A comprehensive machinery maintenance plan should adhere to stringent safety and compliance standards established by regulatory bodies, such as OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and ISO (International Organization for Standardization). Regular inspections of critical components, including hydraulic systems, electrical wiring, and safety guards, are necessary to mitigate risks of workplace injuries. Implementation of a preventive maintenance schedule, incorporating tasks like lubrication, part replacement, and functionality testing, can extend machinery lifespan while ensuring operational efficiency. Proper documentation of maintenance activities, including date, personnel involved, and specific interventions performed, is crucial for compliance audits and enhancing safety protocols. Training sessions for staff on safety practices and emergency procedures must occur periodically to reinforce a culture of safety within the operational environment.
Letter Template For Machinery Maintenance Plan Samples
Letter template of machinery maintenance plan for manufacturing equipment

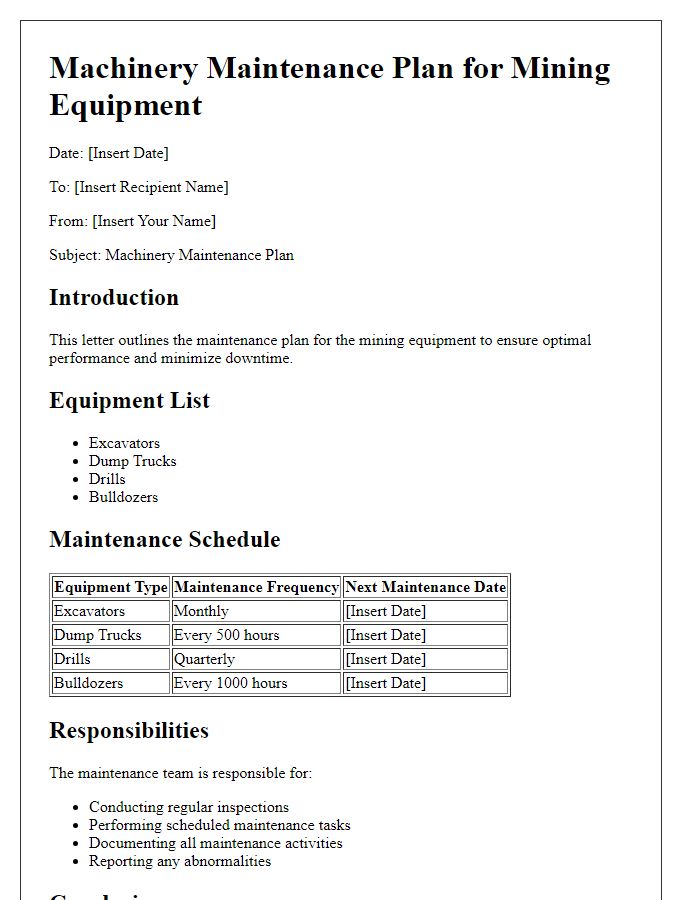
Letter template of machinery maintenance plan for agricultural machinery

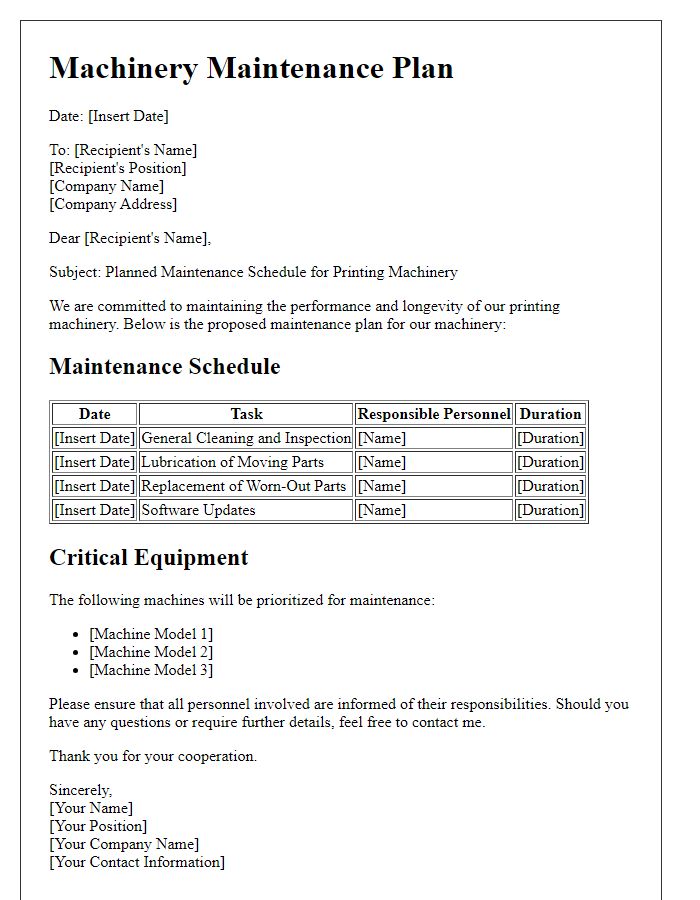
Letter template of machinery maintenance plan for factory automation systems

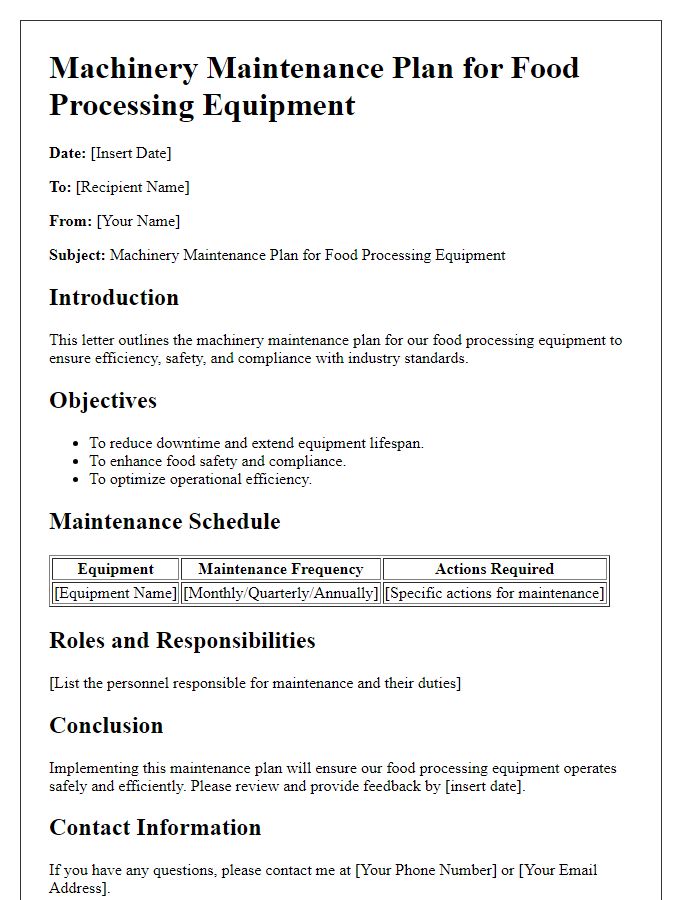
Letter template of machinery maintenance plan for food processing equipment







Comments