Are you waiting anxiously for your health screening results? It can feel like a rollercoaster of emotions, and knowing how to interpret those results is essential for your well-being. This article will walk you through the typical components of health screening reports, demystifying the medical jargon and providing clarity on what it all means for you. Stay with us as we explore how to navigate your results and improve your health journey!

Personal Identification and Contact Information
Health screening results require clear presentation of personal identification and contact information. Personal identification includes full name (e.g., John Doe), date of birth (e.g., April 15, 1990), and patient ID number (e.g., 123456). Contact information encompasses current address (e.g., 123 Elm Street, Springfield, IL), phone number (e.g., (555) 123-4567), and email address (e.g., john.doe@email.com). Including these details ensures accuracy in records and allows healthcare providers to reach patients effectively for follow-up consultations or additional testing, improving overall patient care outcomes. Proper documentation enhances communication for future health-related appointments and inquiries.
Summary of Screening Findings
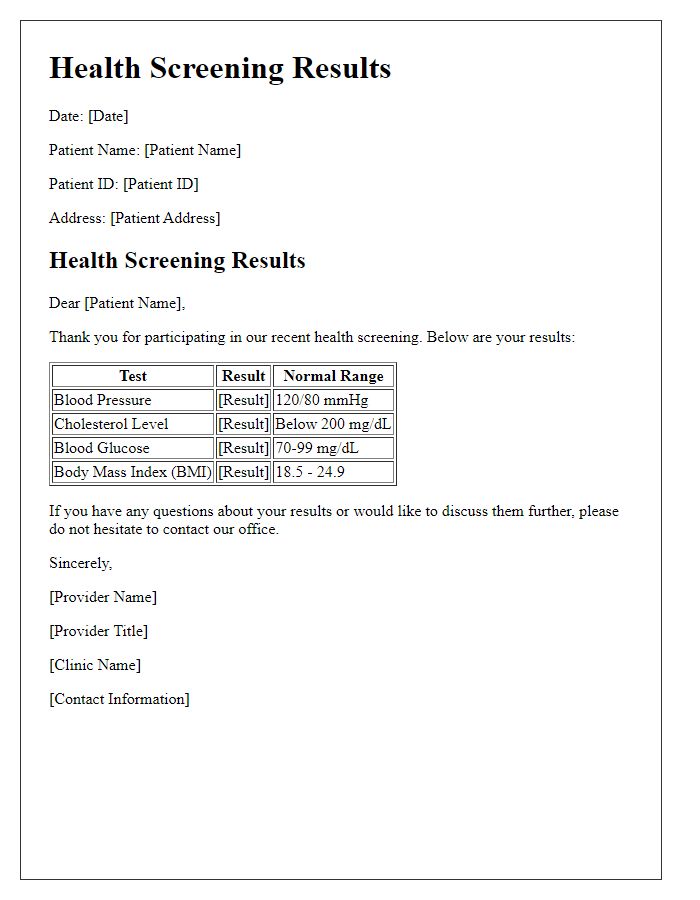
The health screening report provides crucial insights into overall well-being, including metrics such as blood pressure (normal range: 90/60 mmHg to 120/80 mmHg), cholesterol levels (total cholesterol ideally below 200 mg/dL), and blood glucose levels (normal fasting range: 70-99 mg/dL). Key findings might highlight potential risk factors, such as elevated Body Mass Index (BMI) beyond 25 kg/m2, which can indicate overweight or obesity. Additional tests, including cholesterol subtypes (LDL and HDL), can assess cardiovascular health risks and inform lifestyle modifications. The report may also suggest follow-up appointments for further evaluation of conditions like hypertension or diabetes, emphasizing the importance of regular screenings in maintaining long-term health.
Detailed Results Explanation
Health screening results provide a comprehensive overview of an individual's health status, highlighting key metrics such as cholesterol levels, blood pressure, body mass index (BMI), and glucose levels. Cholesterol levels indicate heart health, with total cholesterol ideally under 200 mg/dL. Blood pressure readings, measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg), should ideally be below 120/80 for optimal cardiovascular health. BMI, calculated from weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared, ideally ranges from 18.5 to 24.9 for normal weight. Glucose levels, measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), should be under 100 mg/dL for fasting tests to maintain metabolic health. Abnormal values necessitate follow-up testing and lifestyle modifications to mitigate potential health risks. Regular screenings facilitate early detection of conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia, promoting proactive health management.
Recommended Follow-Up Actions
Health screening results indicate potential concerns that require timely follow-up actions. For example, elevated cholesterol levels (over 240 mg/dL) may necessitate dietary modifications, exercise plans, or medication consultation with a healthcare provider. Abnormal blood pressure readings (systolic above 130 mmHg or diastolic above 80 mmHg) suggest monitoring and lifestyle adjustments to mitigate cardiovascular risks. Additionally, if fasting glucose levels exceed 100 mg/dL, follow-up for potential prediabetes is recommended, potentially involving referrals to nutritionists or diabetes educators. Routine screenings for certain age groups (such as mammograms for women over 40 or PSA tests for men over 50) should also be consistently emphasized to maintain optimal health. Regular follow-up appointments can ensure that any identified issues are addressed proactively, promoting overall well-being.
Privacy and Confidentiality Assurance
Health screening results can include sensitive personal information, making privacy and confidentiality paramount. Health insurance portability and accountability laws (HIPAA) ensure protection against unauthorized access or disclosure of patient information. Secure methods of communication should be employed, including password-protected emails or encrypted databases, to deliver results. Medical facilities must implement policies to limit access to authorized personnel only, safeguarding patient confidentiality throughout the process. Moreover, proper training of staff on confidentiality protocols is essential in maintaining trust and compliance with regulatory standards. Awareness of potential breaches and the importance of reporting them should be integral to healthcare operations.
Letter Template For Health Screening Results Samples
Letter template of health screening results for corporate wellness programs.

Letter template of health screening results for annual health check-ups.

Letter template of health screening results for educational institutions.
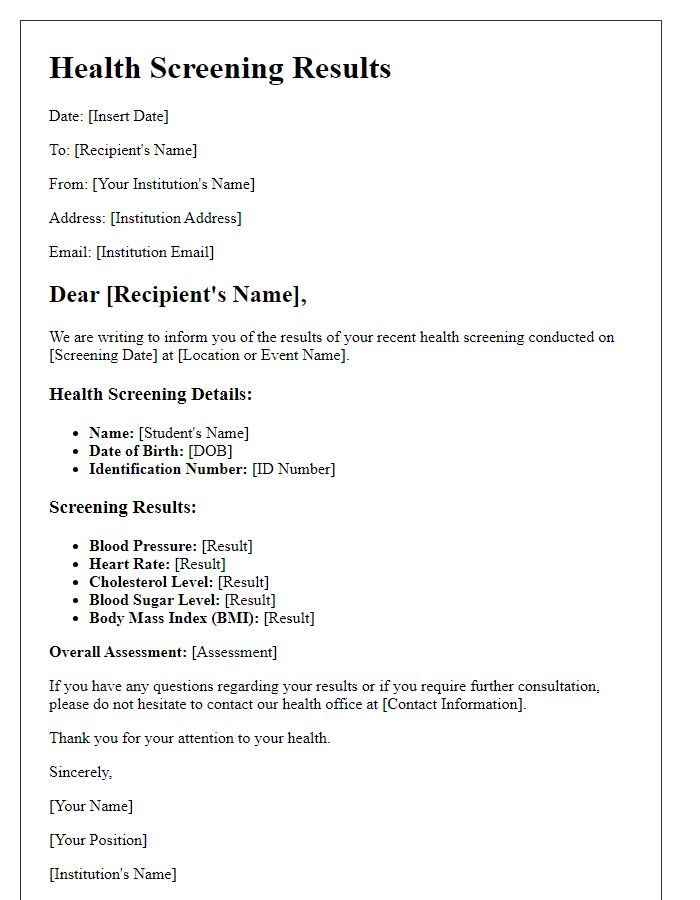
Letter template of health screening results for community health initiatives.

Letter template of health screening results for specific health conditions.








Comments